Naturally occurring single amino acid replacements in a regulatory protein alter streptococcal gene expression and virulence in mice
- PMID: 21490401
- PMCID: PMC3083769
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI45169
Naturally occurring single amino acid replacements in a regulatory protein alter streptococcal gene expression and virulence in mice
Abstract
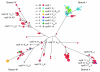
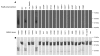
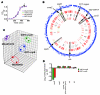
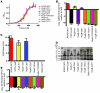
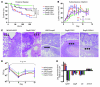
Infection with different strains of the same species of bacteria often results in vastly different clinical outcomes. Despite extensive investigation, the genetic basis of microbial strain-specific virulence remains poorly understood. Recent whole-genome sequencing has revealed that SNPs are the most prevalent form of genetic diversity among different strains of the same species of bacteria. For invasive serotype M3 group A streptococci (GAS) strains, the gene encoding regulator of proteinase B (RopB) has the highest frequency of SNPs. Here, we have determined that ropB polymorphisms alter RopB function and modulate GAS host-pathogen interactions. Sequencing of ropB in 171 invasive serotype M3 GAS strains identified 19 distinct ropB alleles. Inactivation of the ropB gene in strains producing distinct RopB variants had dramatically divergent effects on GAS global gene expression. Additionally, generation of isoallelic GAS strains differing only by a single amino acid in RopB confirmed that variant proteins affected transcript levels of the gene encoding streptococcal proteinase B, a major RopB-regulated virulence factor. Comparison of parental, RopB-inactivated, and RopB isoallelic strains in mouse infection models demonstrated that ropB polymorphisms influence GAS virulence and disease manifestations. These data detail a paradigm in which unbiased, whole-genome sequence analysis of populations of clinical bacterial isolates creates new avenues of productive investigation into the pathogenesis of common human infections.
Figures

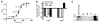
References
-
- Davies HD, et al. Invasive group A streptococcal infections in Ontario, Canada. Ontario Group A Streptococcal Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1996;335(8):547–554. - PubMed
-
- Laupland KB, Gregson DB, Church DL, Ross T, Pitout JD. Incidence, risk factors and outcomes of Escherichia coli bloodstream infections in a large Canadian region. . Clin Microbiol Infect. 2008;14(11):1041–1047. - PubMed
-
- Bae IG, et al. Presence of genes encoding the Panton-Valentine leukocidin exotoxin is not the primary determinant of outcome in patients with complicated skin and skin structure infections due to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus: results of a multinational trial. . J Clin Microbiol. 2009;47(12):3952–3957. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01643-09. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

