Conservative management of placenta accreta in a multiparous woman
- PMID: 21490740
- PMCID: PMC3065870
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/329618
Conservative management of placenta accreta in a multiparous woman
Abstract
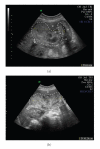
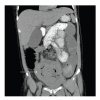
Placenta accreta refers to any abnormally invasive placental implantation. Diagnosis is suspected postpartum with failed delivery of a retained placenta. Massive obstetrical hemorrhage is a known complication, often requiring peripartum hysterectomy. We report a case of presumed placenta accreta in a patient following failed manual removal of a retained placenta. We describe an attempt at conservative management with methotrexate in a stable patient desiring future fertility. Treatment was unsuccessful and led to the development of a disseminated intrauterine infection complicated by a bowel obstruction, requiring both a hysterectomy and small bowel resection. In hemodynamically stable patients, conservative management of placenta accreta may involve leaving placental tissue in situ with subsequent administration of methotrexate. However, ongoing close observation is required to identify complications.
Figures
References
-
- Oyelese Y, Smulian JC. Placenta previa, placenta accreta, and vasa previa. Obstetrics and Gynecology. 2006;107(4):927–941. - PubMed
-
- Miller DA, Chollet JA, Goodwin TM. Clinical risk factors for placenta previa-placenta accreta. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology. 1997;177(1):210–214. - PubMed
-
- Wu S, Kocherginsky M, Hibbard JU. Abnormal placentation: twenty-year analysis. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology. 2005;192(5):1458–1461. - PubMed
-
- Zelop C, Nadel A, Frigoletto FD, Jr., Pauker S, MacMillan M, Benacerraf BR. Placenta accreta/percreta/increta: a cause of elevated maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein. Obstetrics and Gynecology. 1992;80(4):693–694. - PubMed
-
- Tong SYP, Tay KH, Kwek YCK. Conservative management of placenta accreta: review of three cases. Singapore Medical Journal. 2008;49(6):e156–e159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

