Postoperative renal function in patients is unaltered after robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy
- PMID: 21490821
- PMCID: PMC3071483
- DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2011.60.3.192
Postoperative renal function in patients is unaltered after robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy
Abstract
Background: Pneumoperitoneum with an intra-abdominal pressure (IAP) of 14 mmHg is known to decrease renal function. Robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP) requires an IAP of more than 15 mmHg for operation. Therefore, we retrospectively investigated whether patients who underwent RARP experienced renal insufficiency during the postoperative period (at postoperative days 7 and 30).
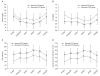
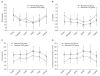
Methods: One hundred patients who underwent RARP were enrolled in this study. Preoperative serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine (Cr) levels were measured. Creatinine clearance (CrCl) was calculated using the Cockcroft and Gault formula. CrCl was calculated at 1 day before surgery (baseline), 2 hr postoperatively, and at 1, 3, 7, and 30 days postoperatively (POD 1, POD 3, POP 7, and POD 30). Patients were assigned to abnormal CrCl (n = 52) or normal CrCl groups (n = 48) on the basis of these measurements.
Results: Significant inter-group differences in BUN, Cr, and CrCl were observed at all postoperative time points. BUN and Cr decreased significantly at postoperative 2 hr and POD 1, 3, and 7 versus baseline in both groups, whereas CrCl increased significantly at postoperative 2 hr and POD 1, 3, and 7 versus baseline in both groups. However, BUN, Cr, and CrCl were similar at POD 30 and preoperatively in the two groups.
Conclusions: RAPR, which requires an IAP of 15-20 mmHg for more than 4 hr, does not induce renal dysfunction during the postoperative period, and even in those patients with an abnormal CrCl.
Keywords: Pneumoperitoneum; Renal function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of renal insufficiency on outcome following infrarenal aortic surgery.Am J Surg. 1997 Aug;174(2):126-30. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(97)00069-x. Am J Surg. 1997. PMID: 9293827
-
Serum creatinine and estimated creatinine clearance do not predict perioperatively measured creatinine clearance in neonates undergoing congenital heart surgery.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2003 Jan;4(1):55-9. doi: 10.1097/00130478-200301000-00011. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2003. PMID: 12656544 Clinical Trial.
-
The impact of aortic endografts on renal function.J Vasc Surg. 2005 Jun;41(6):926-30. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2005.02.024. J Vasc Surg. 2005. PMID: 15944586
-
Estimated creatinine clearance instead of plasma creatinine level as prognostic test for postoperative renal function in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2006 Apr;29(4):461-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2006.01.024. Epub 2006 Feb 17. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2006. PMID: 16483789
-
Functional range of creatinine clearance for renal drug dosing: a practical solution to the controversy of which weight to use in the Cockcroft-Gault equation.Ann Pharmacother. 2013 Jul-Aug;47(7-8):1039-44. doi: 10.1345/aph.1S176. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Ann Pharmacother. 2013. PMID: 23757387 Review.
Cited by
-
Transient acute kidney injury observed immediately after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy but not after open radical prostatectomy.Mol Clin Oncol. 2020 Sep;13(3):18. doi: 10.3892/mco.2020.2087. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Mol Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32754332 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of the Duration of Restrictive Fluid Therapy on Acute Kidney Injury in Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy.J Pers Med. 2023 Nov 28;13(12):1666. doi: 10.3390/jpm13121666. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 38138893 Free PMC article.
-
Transperitoneal versus extraperitoneal robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy on postoperative hepatic and renal function.Gland Surg. 2020 Jun;9(3):759-766. doi: 10.21037/gs-20-533. Gland Surg. 2020. PMID: 32775266 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison between ketorolac- and fentanyl-based patient-controlled analgesia for acute kidney injury after robot-assisted radical prostatectomy: a retrospective propensity score-matched analysis.World J Urol. 2023 May;41(5):1437-1444. doi: 10.1007/s00345-023-04374-3. Epub 2023 Apr 1. World J Urol. 2023. PMID: 37004573
-
Comparison of renal function after robot - assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy versus retropubic radical prostatectomy.Int Braz J Urol. 2019 Jan-Feb;45(1):83-88. doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2018.0103. Int Braz J Urol. 2019. PMID: 29757580 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bishara B, Karram T, Khatib S, Ramadan R, Schwartz H, Hoffman A, et al. Impact of pneumoperitoneum on renal perfusion and excretory function: beneficial effects of nitroglycerine. Surg Endosc. 2009;23:568–576. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen NT, Perez RV, Fleming N, Rivers R, Wolfe BM. Effect of prolonged pneumoperitoneum on intraoperative urine output during laparoscopic gastric bypass. J Am Coll Surg. 2002;195:476–483. - PubMed
-
- McDougall EM, Monk TG, Wolf JS, Jr, Hicks M, Clayman RV, Gardner S, et al. The effect of prolonged pneumoperitoneum on renal function in an animal model. J Am Coll Surg. 1996;182:317–328. - PubMed
-
- Koivusalo AM, Kellokumpu I, Scheinin M, Tikkanen I, Halme L, Lindgren L. Randomized comparison of the neuroendocrine response to laparoscopic cholecystectomy using either conventional or abdominal wall lift techniques. Br J Surg. 1996;83:1532–1536. - PubMed
-
- Sassa N, Hattori R, Yamamoto T, Kato M, Komatsu T, Matsukawa Y, et al. Direct visualization of renal hemodynamics affected by carbon dioxide-induced pneumoperitoneum. Urology. 2009;73:311–315. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

