The anti-metastatic nm23-1 gene is needed for the final step of mammary duct maturation of the mouse nipple
- PMID: 21490937
- PMCID: PMC3072419
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018645
The anti-metastatic nm23-1 gene is needed for the final step of mammary duct maturation of the mouse nipple
Abstract
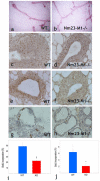
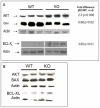
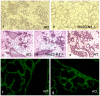
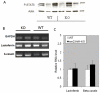
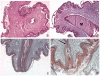
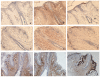
Nm23/NDP kinases are multifunctional enzymes involved in the general homeostasis of triphosphate nucleosides. Numerous studies have shown that NDPKs also serve as regulatory factors of various cell activities, not always connected to nucleotide phosphorylation. In particular, the nme-1 gene, encoding the NM23-1/NDPKA protein, has been reported as a metastasis suppressor gene. This activity was validated in hepatocellular tumors induced in nm23-1 deficient mice. Yet, data describing the primary physiological functions of nm23-1/NDPKA is still scarce. We have characterized in depth the phenotype of nm23-1 deletion in the mammary gland in mice carrying whole body nm23-M1 invalidation. We also asked why the nm23-M1⁻/⁻ mutant females displayed severe nursing disability. We found that the growth retardation of mutant virgin glands was due to reduced proliferation and apoptosis of the epithelial cells within the terminal end buds. The balance of pro/anti-apoptotic factors was impaired in comparison with wild type glands. In the lactating glands, the reduced proliferation rate persisted, but the apoptotic factors were unchanged. However, those defects did not seem to affect the gland maturation since the glands lacking nm23-1/NDPKA appeared morphologically normal. Thorough examination of all the functional aspects of the mammary glands revealed that lack of nm23-1/NDPKA does not impact the production or the ejection of milk in the lumen of lobuloalveolae. Interestingly, an epithelial plug was found to obstruct the extremity of the unique lactiferous duct delivering the milk out of the nipple. These cells, normally disappearing after lactation takes place, persisted in the mutant nipples. This work provides a rare instance of nm23-1/NDPKA physiological functions in the mammary glands and reveals its implication as a modulator factor of proliferation and apoptosis in this tissue.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Boissan M, Dabernat S, Peuchant E, Schlattner U, Lascu I, et al. The mammalian Nm23/NDPK family: from metastasis control to cilia movement. Mol Cell Biochem. 2009;329:51–62. - PubMed
-
- Steeg PS, Bevilacqua G, Sobel ME, Liotta LA. Identification and characterization of differentially expressed genes in tumor metastasis: the nm23 gene. Basic Life Sci. 1991;57:355–360; discussion 360-351. - PubMed
-
- Steeg PS, Bevilacqua G, Kopper L, Thorgeirsson UP, Talmadge JE, et al. Evidence for a novel gene associated with low tumor metastatic potential. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1988;80:200–204. - PubMed
-
- Boissan M, Wendum D, Arnaud-Dabernat S, Munier A, Debray M, et al. Increased lung metastasis in transgenic NM23-Null/SV40 mice with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97:836–845. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

