Olmesartan/amlodipine: a review of its use in the management of hypertension
- PMID: 21490944
- PMCID: PMC3072742
- DOI: 10.2147/VHRM.S16852
Olmesartan/amlodipine: a review of its use in the management of hypertension
Abstract
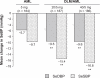
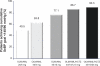
Combination therapy is an effective strategy to increase antihypertensive efficacy in those patients with poor blood pressure (BP) control. In order to achieve BP targets, at least 75% of patients may require combination therapy, and European guidelines advocate this approach, particularly in those patients with a high cardiovascular risk. Evidence from large, randomized controlled trials, and the European hypertension treatment guidelines is supportive of the use of an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) with a calcium channel blocker (CCB). Fixed-dose combination formulations of olmesartan medoxomil, an ARB, and the CCB amlodipine are approved in several European countries for patients with essential hypertension. The olmesartan/amlodipine combination has demonstrated greater efficacy than its component monotherapies in reducing BP in patients with mild-to-severe hypertension. Significantly greater reductions in seated diastolic BP were observed between baseline and after eight weeks of treatment with olmesartan/amlodipine, compared with equivalent doses of olmesartan or amolodipine monotherapy (P < 0.001), in the factorial Combination of Olmesartan Medoxomil and Amlodipine Besylate in Controlling High Blood Pressure (COACH) trial. About 85% of the maximal BP reductions after the 8-week treatment period were already observed after two weeks. Uptitration as necessary, with or without hydrochlorothiazide, allowed the majority of patients to achieve BP control in a 44-week open-label extension treatment period to the COACH trial. The use of olmesartan/amlodipine allowed up to 54% of patients, with previously inadequate responses to amlodipine or olmesartan monotherapy, to achieve their BP goals. Data from post-registration studies using tight BP control and forced titration regimens have further demonstrated the high efficacy of olmesartan/amlodipine in achieving BP goal rates. Moreover, consistent reductions in BP were observed over the 24-hour dosing interval using ambulatory measurements. Olmesartan/amlodipine was generally well tolerated over the short- and long-term, with a lower frequency of peripheral edema with olmesartan/amlodipine 40/10 mg than with amlodipine 10 mg monotherapy.
Keywords: BP control; BP goals; antihypertensive monotherapy; combination therapy; hypertension; patients.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Efficacy and tolerability of olmesartan medoxomil combined with amlodipine in patients with moderate to severe hypertension after amlodipine monotherapy: a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, multicentre study.Clin Drug Investig. 2009;29(1):11-25. doi: 10.2165/0044011-200929010-00002. Clin Drug Investig. 2009. PMID: 19067471 Clinical Trial.
-
Olmesartan medoxomil plus amlodipine increases efficacy in patients with moderate-to-severe hypertension after monotherapy: a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, multicentre study.Clin Drug Investig. 2009;29(7):427-439. doi: 10.2165/00044011-200929070-00001. Clin Drug Investig. 2009. PMID: 19499960 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of a stepped-care regimen using olmesartan medoxomil, amlodipine and hydrochlorothiazide in patients with moderate-to-severe hypertension: an open-label, long-term study.Clin Drug Investig. 2009;29(6):381-91. doi: 10.2165/00044011-200929060-00002. Clin Drug Investig. 2009. PMID: 19432498 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of fixed-dose combination therapy in the treatment of patients with hypertension: focus on amlodipine/valsartan.Clin Drug Investig. 2010;30(9):625-41. doi: 10.2165/11538440-000000000-00000. Clin Drug Investig. 2010. PMID: 20626210 Review.
-
Olmesartan medoxomil combined with hydrochlorothiazide for the treatment of hypertension.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2006;2(4):401-9. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.2006.2.4.401. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2006. PMID: 17323594 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of antihypertensive treatment on 24-h blood pressure variability: pooled individual data analysis of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring studies based on olmesartan mono or combination treatment.J Hypertens. 2018 Apr;36(4):720-733. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001608. J Hypertens. 2018. PMID: 29045341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles of a fixed-dose combination of olmesartan medoxomil and amlodipine in healthy Chinese males and females.Clin Drug Investig. 2012 Dec;32(12):783-90. doi: 10.1007/s40261-012-0026-0. Clin Drug Investig. 2012. PMID: 23160920 Clinical Trial.
-
Phototransformation of amlodipine: degradation kinetics and identification of its photoproducts.PLoS One. 2014 Oct 3;9(10):e109206. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109206. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25279815 Free PMC article.
-
Design of Olmesartan Medoxomil-Loaded Nanosponges for Hypertension and Lung Cancer Treatments.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Jul 11;13(14):2272. doi: 10.3390/polym13142272. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34301030 Free PMC article.
-
Hypertension: Synergy of antihypertensives in elderly patients with CKD.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2013 Jan;9(1):13-5. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2012.264. Epub 2012 Nov 27. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23183840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ezzati M, Lopez AD, Rodgers A, Vander Hoorn S, Murray CJ. Selected major risk factors and global and regional burden of disease. Lancet. 2002;360(9343):1347–1360. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Reducing Risks, Promoting Healthy Life The World Health Report. Available at: http://www.who.int/whr/2002/en/whr02_en.pdf. Accessed September 17, 2008.
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005;365(9455):217–223. - PubMed
-
- Ong KL, Cheung BM, Man YB, Lau CP, Lam KS. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension among United States adults 1999–2004. Hypertension. 2007;49(1):69–75. - PubMed
-
- Wolf-Maier K, Cooper RS, Banegas JR, et al. Hypertension prevalence and blood pressure levels in 6 European countries, Canada, and the United States. JAMA. 2003;289(18):2363–2369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

