SLO-1-channels of parasitic nematodes reconstitute locomotor behaviour and emodepside sensitivity in Caenorhabditis elegans slo-1 loss of function mutants
- PMID: 21490955
- PMCID: PMC3072372
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1001330
SLO-1-channels of parasitic nematodes reconstitute locomotor behaviour and emodepside sensitivity in Caenorhabditis elegans slo-1 loss of function mutants
Abstract
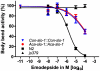
The calcium-gated potassium channel SLO-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans was recently identified as key component for action of emodepside, a new anthelmintic drug with broad spectrum activity. In this study we identified orthologues of slo-1 in Ancylostoma caninum, Cooperia oncophora, and Haemonchus contortus, all important parasitic nematodes in veterinary medicine. Furthermore, functional analyses of these slo-1 orthologues were performed using heterologous expression in C. elegans. We expressed A. caninum and C. oncophora slo-1 in the emodepside-resistant genetic background of the slo-1 loss-of-function mutant NM1968 slo-1(js379). Transformants expressing A. caninum slo-1 from C. elegans slo-1 promoter were highly susceptible (compared to the fully emodepside-resistant slo-1(js379)) and showed no significant difference in their emodepside susceptibility compared to wild-type C. elegans (p = 0.831). Therefore, the SLO-1 channels of A. caninum and C. elegans appear to be completely functionally interchangeable in terms of emodepside sensitivity. Furthermore, we tested the ability of the 5' flanking regions of A. caninum and C. oncophora slo-1 to drive expression of SLO-1 in C. elegans and confirmed functionality of the putative promoters in this heterologous system. For all transgenic lines tested, expression of either native C. elegans slo-1 or the parasite-derived orthologue rescued emodepside sensitivity in slo-1(js379) and the locomotor phenotype of increased reversal frequency confirming the reconstitution of SLO-1 function in the locomotor circuits. A potent mammalian SLO-1 channel inhibitor, penitrem A, showed emodepside antagonising effects in A. caninum and C. elegans. The study combined the investigation of new anthelmintic targets from parasitic nematodes and experimental use of the respective target genes in C. elegans, therefore closing the gap between research approaches using model nematodes and those using target organisms. Considering the still scarcely advanced techniques for genetic engineering of parasitic nematodes, the presented method provides an excellent opportunity for examining the pharmacofunction of anthelmintic targets derived from parasitic nematodes.
Conflict of interest statement
Achim Harder is employed by BayerHealthCare AG, which is developing veterinary pharmaceuticals including antiparasiticdal drugs like emodepside. This study was performed as a collaborative research project between Bayer HealthCare AG and the Institute for Parasitology and Tropical Veterinary Medicine, Freie Universität Berlin as well as previously the Institute for Parasitology at the University of Veterinary Medicine, Hannover. Accordingly, both academic institutions received project specific reseach grants from Bayer HealthCare AG.
Figures




References
-
- Jasmer DP, Goverse A, Smant G. Parasitic nematode interactions with mammals and plants. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2003;41:245–270. - PubMed
-
- Wolstenholme AJ, Fairweather I, Prichard R, Samson-Himmelstjerna G, Sangster NC. Drug resistance in veterinary helminths. Trends Parasitol. 2004;20:469–476. - PubMed
-
- De Clercq D, Sacko M, Behnke J, Gilbert F, Dorny P, et al. Failure of mebendazole in treatment of human hookworm infections in the southern region of Mali. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1997;57:25–30. - PubMed
-
- Reynoldson JA, Behnke JM, Pallant LJ, Macnish MG, Gilbert F, et al. Failure of pyrantel in treatment of human hookworm infections (Ancylostoma duodenale) in the Kimberley region of north west Australia. Acta Trop. 1997;68:301–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

