Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 clade B and C gp120 differentially induce neurotoxin arachidonic acid in human astrocytes: implications for neuroAIDS
- PMID: 21491143
- PMCID: PMC5737634
- DOI: 10.1007/s13365-011-0026-5
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 clade B and C gp120 differentially induce neurotoxin arachidonic acid in human astrocytes: implications for neuroAIDS
Abstract
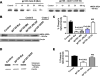
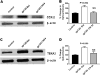
HIV-1 clades (subtypes) differentially contribute to the neuropathogenesis of HIV-associated dementia (HAD) in neuroAIDS. HIV-1 envelop protein, gp120, plays a major role in neuronal function. It is not well understood how these HIV-1 clades exert these neuropathogenic differences. The N-methyl-D: -aspartate (NMDA) receptor-reduced glutamine synthesis could lead to secretion of neurotoxins such as arachidonic acid (AA) which plays a significant role in the neuropathogenic mechanisms in neuroAIDS. We hypothesize that clade B and C gp120 proteins exert differential effects on human primary astrocytes by production of the neurotoxin arachidonic acid. Our results indicate that clade B gp120 significantly downregulated NMDA receptor gene and protein expression, and level of glutamine while increasing expression of prostaglandin E2 (PGE(2)) and thromboxane A2 receptor (TBXA(2) R) compared to HIV-1 clade C gp120 protein. Thus, our studies for the first time demonstrate that HIV-1 clade B-gp120 protein appears to induce higher levels of expression of the neuropathogenic molecule cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)-mediated arachidonic acid by-products, PGE(2), and TBXA(2) R compared to HIV-1 clade C gp120 protein. These studies suggest that HIV-1 clade B and C gp120 proteins may play a differential role in the neuropathogenesis of HAD in neuroAIDS.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



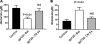
Similar articles
-
Differential regulation of indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) by HIV type 1 clade B and C Tat protein.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2009 Mar;25(3):329-35. doi: 10.1089/aid.2008.0225. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2009. PMID: 19327051 Free PMC article.
-
The role of arachidonic acid in the regulation of nitric oxide synthase isoforms by HIV gp120 protein in astroglial cells.Free Radic Biol Med. 2014 Sep;74:14-20. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.06.009. Epub 2014 Jun 19. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 24953535
-
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 clade B and C Tat differentially induce indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and serotonin in immature dendritic cells: Implications for neuroAIDS.J Neurovirol. 2010 Jul;16(4):255-63. doi: 10.3109/13550284.2010.497809. J Neurovirol. 2010. PMID: 20602605
-
Differential regulation of neurotoxin in HIV clades: role of cocaine and methamphetamine.Curr HIV Res. 2012 Jul;10(5):429-34. doi: 10.2174/157016212802138742. Curr HIV Res. 2012. PMID: 22591367 Review.
-
HIV-related neurotoxicity.Brain Pathol. 1991 Apr;1(3):193-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1991.tb00659.x. Brain Pathol. 1991. PMID: 1669708 Review.
Cited by
-
Arachidonic Acid Cascade and Eicosanoid Production Are Elevated While LTC4 Synthase Modulates the Lipidomics Profile in the Brain of the HIVgp120-Transgenic Mouse Model of NeuroHIV.Cells. 2022 Jul 5;11(13):2123. doi: 10.3390/cells11132123. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35805207 Free PMC article.
-
HIV Subtypes B and C gp120 and Methamphetamine Interaction: Dopaminergic System Implicates Differential Neuronal Toxicity.Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 9;5:11130. doi: 10.1038/srep11130. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26057350 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroimaging markers of human immunodeficiency virus infection in South Africa.J Neurovirol. 2012 Jun;18(3):151-6. doi: 10.1007/s13365-012-0090-5. Epub 2012 Apr 12. J Neurovirol. 2012. PMID: 22528474 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Tat and cocaine impact mitochondrial epigenetics: effects on DNA methylation.Epigenetics. 2021 Sep;16(9):980-999. doi: 10.1080/15592294.2020.1834919. Epub 2020 Oct 24. Epigenetics. 2021. PMID: 33100130 Free PMC article.
-
Cocaine Self-Administration Influences Central Nervous System Immune Responses in Male HIV-1 Transgenic Rats.Cells. 2022 Aug 4;11(15):2405. doi: 10.3390/cells11152405. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35954251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brenneman DE, McCune SK, Mervis RF, Hill JM. gp120 as an etiologic agent for neuroAIDS: neurotoxicity and model systems. Adv Neuroimmunol. 1994;4:157–165. - PubMed
-
- Chang J, Jozwiak R, Wang B, Ng T, Ge YC, Bolton W, Dwyer DE, Randle C, Osborn R, Cunningham AL, Saksena NK. Unique HIV type 1 V3 region sequences derived from six different regions of brain: region-specific evolution within host-determined quasispecies. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1998;14:25–30. - PubMed
-
- Choe H, Martin KA, Farzan M, Sodroski J, Gerard NP, Gerard C. Structural interactions between chemokine receptors, gp120 Env and CD4. Semin Immunol. 1998;10:249–257. - PubMed
-
- Corasaniti MT, Melino G, Navarra M, Garaci E, Finazzi-Agro A, Nistico G. Death of cultured neuroblastoma cells induced by HIV-1 gp120 is prevented by NMDA receptor antagonists and inhibitors of nitric oxide and cyclooxygenase. Neurodegeneration. 1995;4:315–321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

