Hydrolysis of bulged nucleotides in hybrids formed by RNA and imidazole-derivatized oligo-2'-O-methylribonucleotides
- PMID: 21491332
- PMCID: PMC3097529
- DOI: 10.1080/15257770.2011.569810
Hydrolysis of bulged nucleotides in hybrids formed by RNA and imidazole-derivatized oligo-2'-O-methylribonucleotides
Abstract
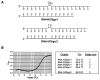
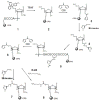
In order to enhance the efficacy of small antisense molecules, we examined a series of antisense oligonucleotides derivatized with functional groups designed to enable them to hydrolyze their RNA target. Solid phase synthetic methods were used to prepare imidazole-derivatized antisense oligo-2'-O-methylribonucleotides. Upon binding, these oligonucleotides create internal bulged bases in the target RNA that serve as sites for hydrolysis. We observed that an oligonucleotide derivatized with a side chain containing two imidazole groups was capable of hydrolyzing 58% of its RNA target when incubated with the target for 48 hours at 37°C and physiological pH.
Figures


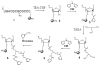

References
-
- Prakash TP, Bhat B. 2′-Modified oligonucleotides for antisense therapeutics. Curr Top Med Chem. 2007;7(7):641–9. - PubMed
-
- Zamaratski E, Pradeepkumar PI, Chattopadhyaya J. A critical survey of the structure-function of the antisense oligo/RNA heteroduplex as substrate for RNase H. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 2001;48(3):189–208. - PubMed
-
- Fabani MM, Turner JJ, Gait MJ. Oligonucleotide analogs as antiviral agents. Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2006;8(2):108–14. - PubMed
-
- Hogrefe HH, Hogrefe RI, et al. Kinetic analysis of Escherichia coli RNase H using DNA-RNA-DNA/DNA substrates. J Biol Chem. 1990;265(10):5561–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
