Oral naltrexone maintenance treatment for opioid dependence
- PMID: 21491383
- PMCID: PMC7045778
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001333.pub4
Oral naltrexone maintenance treatment for opioid dependence
Abstract
Background: Research on clinical application of oral naltrexone agrees on several things. From a pharmacological perspective, naltrexone works. From an applied perspective, the medication compliance and the retention rates are poor.
Objectives: To evaluate the effects of naltrexone maintenance treatment versus placebo or other treatments in preventing relapse in opioid addicts after detoxification.
Search strategy: We searched: Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL - The Cochrane Library issue 6 2010), PubMed (1973- June 2010), CINAHL (1982- June 2010). We inspected reference lists of relevant articles and contacted pharmaceutical producers of naltrexone, authors and other Cochrane review groups.
Selection criteria: All randomised controlled clinical trials which focus on the use of naltrexone maintenance treatment versus placebo, or other treatments to reach sustained abstinence from opiate drugs
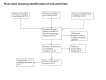
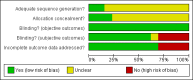
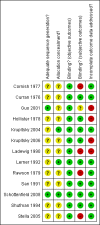
Data collection and analysis: Three reviewers independently assessed studies for inclusion and extracted data. One reviewer carried out the qualitative assessments of the methodology of eligible studies using validated checklists.
Main results: Thirteen studies, 1158 participants, met the criteria for inclusion in this review.Comparing naltrexone versus placebo or no pharmacological treatments, no statistically significant difference were noted for all the primary outcomes considered. The only outcome statistically significant in favour of naltrexone is re incarceration, RR 0.47 (95%CI 0.26-0.84), but results come only from two studies. Considering only studies were patients were forced to adherence a statistical significant difference in favour of naltrexone was found for retention and abstinence, RR 2.93 (95%CI 1.66-5.18).Comparing naltrexone versus psychotherapy, in the two considered outcomes, no statistically significant difference was found in the single study considered.Naltrexone was not superior to benzodiazepines and to buprenorphine for retention and abstinence and side effects. Results come from single studies.
Authors' conclusions: The findings of this review suggest that oral naltrexone did not perform better than treatment with placebo or no pharmacological agent with respect to the number of participants re-incarcerated during the study period. If oral naltrexone is compared with other pharmacological treatments such as benzodiazepine and buprenorphine, no statistically significant difference was found. The percentage of people retained in treatment in the included studies is however low (28%). The conclusion of this review is that the studies conducted have not allowed an adequate evaluation of oral naltrexone treatment in the field of opioid dependence. Consequently, maintenance therapy with naltrexone cannot yet be considered a treatment which has been scientifically proved to be superior to other kinds of treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures












Update of
-
Oral naltrexone maintenance treatment for opioid dependence.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Feb 16;(2):CD001333. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001333.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Apr 13;(4):CD001333. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001333.pub4. PMID: 21328250 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Cornish 1977 {published data only}
-
- Cornish JW, Metzger D, Woody GE, Wilson D, McLellan AT, Vandergrift B, et al. Naltrexone pharmacotherapy for opioid dependent federal probationers. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 1997;14(6):529‐34. - PubMed
Curran 1976 {published data only}
-
- Curran S, Savage C. Patients response to naltrexone: issues of acceptance, treatment effects, and frequency of administration. NIDA Research Monograph Series 1976;9:67‐9. - PubMed
Guo 2001 {published data only}
-
- Guo S, Jiang Z, Wu Y. Efficacy of naltrexone Hydrochloride for preventing relapse among opiate‐dependent patients after detoxification. Hong Kong Journal of Psychiatry 2001;11(4):2‐8.
Hollister 1978 {published data only}
-
- Hollister LE. Clinical evaluation of naltrexone treatment of opiate‐dependent individuals. Report of the National Research Council Committee on Clinical Evaluation of Narcotic Antagonists. Archives of General Psychiatry 1978;35(3):335‐40. - PubMed
Krupitsky 2004 {published data only}
-
- Krupitsky EM, Zvartau EE, Masalov DV, Tsoi MV, Burakov AM, Egorova VY, et al. Naltrexone for heroin dependence treatment in St Petersburg, Russia. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 2004;26(4):285‐94. - PubMed
Krupitsky 2006 {published data only}
-
- Krupitsky EM, Zvartau EE, Masalov DV, Tsoy MV, Burakov AM, Egorova VY, et al. Naltrexone with or without fluoxitine for preventing relapse to heroin addiction in St. Petersburg, Russia. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 2006;31:319‐28. - PubMed
Ladewig 1990 {published data only}
-
- Ladewig D. Naltrexone ‐ an effective aid in the psychosocial rehabilitation process of former opiate dependent patients. Therapeutische Umschau 1990;47(3):247‐50. - PubMed
Lerner 1992 {published data only}
-
- Lerner A, Sigal M, Bacalu A, Shiff R, Burganski I, Gelkopf M. A naltrexone double‐blind placebo controlled study in Israel. Israel Journal of Psychiatry and Related Sciences 1992;29(1):36‐43. - PubMed
Rawson 1979 {published data only}
-
- Rawson RA, Glazer M, Callahan EJ, Liberman RP. Naltrexone and behaviour therapy for heroin addiction. NIDA Research Monograph Series 1979;25:26‐43. - PubMed
San 1991 {published data only}
-
- San L, Pomarol G, Peri JM, Olle JM, Cami J. Follow‐up after a six‐month maintenance period on naltrexone versus placebo in heroin addicts. British Journal of Addiction 1991;86(8):983‐90. - PubMed
Schottenfield 2008 {published data only}
Shufman 1994 {published data only}
-
- Shufman EN, Porat S, Witzum E, Gandacu C, Bar‐Hamburger R, Ginath Y. The efficacy of naltrexone in preventing re abuse of heroin after detoxification. Biological Psychiatry 1994;35(12):935‐45. - PubMed
Stella 2005 {published data only}
-
- Stella L, D'Ambra C, Mazzeo F, Capuano A, Franco F, Avolio A, et al. Nalltrexone plus benzodiazepines aids abstinence in opioid‐dependents patients. Life Science 2005;77:2717‐22. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Altman 1976 {published data only}
-
- Altman JL, Meyer RE, Mirin SM, McNamee HB, McDougle M. Opiate antagonists and the modification of heroin self‐administration behaviour in man: an experimental study. The International Journal of the Addictions 1976;11(3):485‐99. - PubMed
Anton 1981 {published data only}
-
- Anton RA, Hogan I, Jalali B, Riordan CE, Kleber HD. Multiple family therapy and naltrexone in the treatment of opiate dependence. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 1981;8(2):157‐68. - PubMed
Arndt 1984 {published data only}
-
- Arndt I, Lellan AT, O´Brien CP. Abstinence treatments for opiate addicts: therapeutic community or naltrexone?. NIDA Research Monograph Series 1984;49:275‐81. - PubMed
Brahen 1977 {published data only}
-
- Brahen LS, Capone T, Wiechert V, Desiderio D. Naltrexone and cyclazocine. A controlled treatment study. Archives of General Psychiatry 1977;34(10):1181‐4. - PubMed
Brahen 1978 {published data only}
-
- Brahen LS, Capone T, Heller RC, Linden SL, Landy HJ, Lewis MJ. Controlled clinical study of naltrexone side effects comparing first‐day doses and maintenance regimens. American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse 1978;5(2):235‐45. - PubMed
Callahan 1980 {published data only}
-
- Callahan EJ, Rawson RA, McCleave B, Arias R, Glazer M, Liberman RP. The treatment of heroin addiction: naltrexone alone and with behaviour therapy. The International Journal of the Addictions 1980;15(6):795‐807. - PubMed
Crowley 1985 {published data only}
-
- Crowley TJ, Wagner JE, Zerbe G, Macdonald M. Naltrexone‐induced dysphoria in former opioid addicts. American Journal of Psychiatry 1985;142(9):1081‐4. - PubMed
Gerra 1995 {published data only}
-
- Gerra G, Marcato A, Caccavari R, Fontanesi B, Delsignore R, Fertonani G, et al. Clonidine and opiate receptor antagonists in the treatment of heroin addiction. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 1995;12(1):35‐41. - PubMed
Greenstein 1984 {published data only}
-
- Greenstein RA, Arndt IC, McLellan AT, O´Brien CP, Evans B. Naltrexone: a clinical perspective. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1984;45(9):25‐8. - PubMed
Grey 1986 {published data only}
-
- Grey C, Osborn E, Reznikoff M. Psychosocial factors in outcome in two opiate addiction treatments. Journal of Clinical Psychology 1986;42(1):185‐9. - PubMed
Hollister 1977 {published data only}
-
- Hollister LE, Schwin RL, Kasper P. Naltrexone treatment of opiate‐dependent persons. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 1977;2(3):203‐9. - PubMed
Hurzeler 1976 {published data only}
-
- Hurzeler M, Gerwirtz D, Kleber H. Varying clinical contexts for administering naltrexone. NIDA Research Monograph 1976;9:48‐66. - PubMed
Judson 1981 {published data only}
-
- Judson BA, Goldstein A, Inturrisi CE. Methadyl acetate (LAAM) in the treatment of heroin addicts. Archieves of General Psychiatry 1983;40(8):834‐40. - PubMed
Judson 1983 {published data only}
-
- Judson BA, Carney TM, Goldstein A. Naltrexone treatment of heroin addiction: efficacy and safety in a double‐blind dosage comparison. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 1981;7(4):325‐46. - PubMed
Judson 1984 {published data only}
-
- Judson BA, Goldstein A. Naltrexone treatment of heroin addiction: one‐year follow‐up. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 1984;13(4):357‐65. - PubMed
Lewis 1978 {published data only}
-
- Lewis DC, Mayer J, Hersch RG, Black R. Narcotic antagonist treatment: clinical experience with naltrexone. The International Journal of the Addictions 1978;13(6):961‐73. - PubMed
Martin 1973 {published data only}
-
- Martin WR, Jasinski DR, Mansky PA, Lexington K. Naltrexone, an antagonist for the treatment of heroin dependence. Archieves of General Psychiatry 1973;28(6):784‐91. - PubMed
Mello 1981 {published data only}
-
- Mello NK, Mendelson JH, Kuehnle JC, Sellers MS. Operant analysis of human heroin self‐administration and the effects of naltrexone. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 1981;216(1):45‐54. - PubMed
Navaratnam 1994 {published data only}
-
- Navaratnam V, Jamaludin A, Narayanasamy R, Mohamed M, Mansor SM. Determination of naltrexone dosage for narcotic agonist blockade in detoxified Asian addicts. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 1994;34(3):231‐6. - PubMed
Nunes 2006 {published data only}
-
- Nunes, E. V, Rothenberg, J. L, Sullivan, M. A, Carpenter, K. M, Kleber. H. D. Behavioral therapy to augment oral naltrexone for opioid dependence: a ceiling on effectiveness?. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse. 2006;32(4):503‐17. - PubMed
O`Brien 1975 {published data only}
-
- O´Brien CP, Greenstein RA, Mintz J, Woody GE. Clinical experience with naltrexone. American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse 1975;2(3‐4):365‐77. - PubMed
Osborn 1986 {published data only}
-
- Osborn E, Grey C, Reznikoff M. Psychosocial adjustment, modality choice and outcome in naltrexone versus methadone treatment. American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse 1986;12(4):383‐8. - PubMed
Raby 2009 {published data only}
-
- Raby, W. N, Carpenter, K. M, Rothenberg, J, Brooks, A. C, Jiang, H, Sullivan, M, Bisaga, A, Comer, S, Nunes. E. V. Intermittent marijuana use is associated with improved retention in naltrexone treatment for opiate‐dependence.. Am J Addict. 2009 Jul‐2009 Aug 31; 18(4):301‐8 2009;18(4):301‐8. - PMC - PubMed
Rea 2004 {published data only}
-
- Rea F, Bell JR, Young MR, Mattick RP. A randomised, controlled trial of low dose naltrexone for the treatment of opioid dependence. Drug and Alcohol Dependence 2004;75(1):79‐88. - PubMed
Resnick 1974 {published data only}
-
- Resnick RB, Volavka J, Freedman AM, Thomas M. Studies of EN‐1639A (Naltrexone): a new narcotic antagonist. American Journal of Psychiatry 1974;131(6):646‐50. - PubMed
Rothenberg 2002 {published data only}
-
- Rothenberg JL, Sullivan MA, Church SH, Seracini A, Collins E, Kleber HD, et al. Behavioral naltrexone therapy: Efficacy of a new behavioral treatment for heroin dependence and future directions. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment 2002;23(4):351‐60. - PubMed
Sideroff 1978 {published data only}
-
- Sideroff SI, Charuvastra VC, Jarvik ME. Craving in heroin addicts maintained on the opiate antagonist naltrexone. American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse 1978;5(4):415‐23. - PubMed
Taintor 1975 {published data only}
-
- Taintor Z, Landsberg R, Wicks N. Experiences with naltrexone in Buffalo. American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse 1975;2(3‐4):391‐401. - PubMed
Tennant 1984 {published data only}
-
- Tennant FS, Rawson RA, Cohen AJ, Mann A. Clinical experience with naltrexone in suburban opioid addicts. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1984;45(9):42‐5. - PubMed
Volavka 1976 {published data only}
-
- Volavka J, Resnick RB, Kestenbaum RS, Freedman AM. Short‐term effects of naltrexone in 155 heroin ex‐addicts. Biological Psychiatry 1976;11(6):679‐85. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Grinenko 2003 {published data only}
-
- Grinenko AI, Krupitskii EM, Zvartau EE. Pharmacotherapy in heroin addiction:pharmacological approaches to remission stabilization and recurrence prevention. Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk 2003;10:54‐6. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Blondell 2009 {published data only}
-
- Comparison of Buprenorphine/Naloxone with Naltrexone in opioid dependent patients. Ongoing study October 2009; the study is currently recruiting participants.
Additional references
AIHW 2009
-
- AIHW (Australian Institute of Health and Welfare). Alcohol and other drug treatment services in Australia 2007‐08; report of the national minimum dataset. Cat. no. HSE 73. Canberra 2009.
Amato 2005
-
- Amato L, Davoli M, Ferri M, Ali R. Methadone at tapered doses for the management of opioid withdrawal. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2005, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858] - DOI
Brahen 1984
-
- Brahen LS, Henderson RK, Capone T, Kordal N. Naltrexone treatment in a jail work‐release program. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1984;45(9):49‐52. - PubMed
Clark 2002
EMCDDA 2009
-
- European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction. The state of the drugs problem in Europe. http://www.emcdda.europa.eu/attachements.cfm/att_93236_EN_EMCDDA_AR2009 2009.
Faggiano 2003
Higgins 2008
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.1 [updated September 2008]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2008. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Ling 1984
-
- Ling W, Wesson DR. Naltrexone treatment for addicted health‐care professionals: a collaborative private practice experience. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1984;45(9):46‐8. - PubMed
Lobmaier 2008
Mattick 2008
Mattick 2009
Mc Lellan 2000
-
- McLellan AT, Lewis DC, O'Brien CP, Kleber HD. Drug dependence, a chronic medical illness: implications for treatment, insurance, and outcomes evaluation. JAMA 2000;284(13):1689‐95. - PubMed
O'Connor 2000
-
- O'Connor PG, Fiellin DA. Pharmacological treatment of heroin dependent patients. Annals of Internal Medicine 2000;133(1):40‐54. - PubMed
Preston 1993
-
- Preston KL, Bigelow GE. Differential naltrexone antagonism of hydromorphone and pentazocine effects in human volunteers. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 1193;264(2):813‐23. - PubMed
Rawson 2000
-
- Rawson RA, McCann MJ, Hasson AJ, Ling W. Addiction pharmacotherapy 2000: new options, new challenges. Journal of Pscychoactive Drugs 2000;32(4):371‐7. - PubMed
SAMHSA 2009
-
- Results from the 2008 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: National Findings. NSDUH Series H‐36 HHS publication No SMA09‐4434 Rockville.
Ward 1999
-
- Ward J, Hall, W, Mattick RP. Role of maintenance treatment in opioid dependence. Lancet 1999;353(9148):221‐6. - PubMed
Washton 1984
-
- Washton AM, Pottash AC, Gold MS. Naltrexone in addicted business executives and physicians. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 1984;45(9):39‐41. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Kirchmayer 1999
-
- Kirchmayer U, Davoli M, Verster A. Naltrexone maintenance treatment for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 1999, Issue 1. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858] - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

