Distribution and physiological effects of B-type allatostatins (myoinhibitory peptides, MIPs) in the stomatogastric nervous system of the crab Cancer borealis
- PMID: 21491432
- PMCID: PMC3245975
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.22654
Distribution and physiological effects of B-type allatostatins (myoinhibitory peptides, MIPs) in the stomatogastric nervous system of the crab Cancer borealis
Abstract
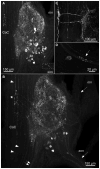
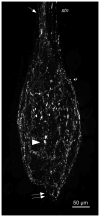
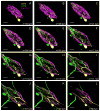
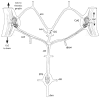
The crustacean stomatogastric ganglion (STG) is modulated by a large number of amines and neuropeptides that are found in descending pathways from anterior ganglia or reach the STG via the hemolymph. Among these are the allatostatin (AST) B types, also known as myoinhibitory peptides (MIPs). We used mass spectrometry to determine the sequences of nine members of the AST-B family of peptides that were found in the stomatogastric nervous system of the crab Cancer borealis. We raised an antibody against Cancer borealis allatostatin-B1 (CbAST-B1; VPNDWAHFRGSWa) and used it to map the distribution of CbAST-B1-like immunoreactivity (-LI) in the stomatogastric nervous system. CbAST-B1-LI was found in neurons and neuropil in the commissural ganglia (CoGs), in somata in the esophageal ganglion (OG), in fibers in the stomatogastric nerve (stn), and in neuropilar processes in the STG. CbAST-B1-LI was blocked by preincubation with 10(-6) M CbAST-B1 and was partially blocked by lower concentrations. Electrophysiological recordings of the effects of CbAST-B1, CbAST-B2, and CbAST-B3 on the pyloric rhythm of the STG showed that all three peptides inhibited the pyloric rhythm in a state-dependent manner. Specifically, all three peptides at 10(-8) M significantly decreased the frequency of the pyloric rhythm when the initial frequency of the pyloric rhythm was below 0.6 Hz. These data suggest important neuromodulatory roles for the CbAST-B family in the stomatogastric nervous system.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mass spectrometric characterization and physiological actions of VPNDWAHFRGSWamide, a novel B type allatostatin in the crab, Cancer borealis.J Neurochem. 2007 May;101(4):1099-107. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04482.x. Epub 2007 Mar 29. J Neurochem. 2007. PMID: 17394556
-
Mass spectrometric characterization and physiological actions of novel crustacean C-type allatostatins.Peptides. 2009 Sep;30(9):1660-8. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2009.05.023. Epub 2009 Jun 6. Peptides. 2009. PMID: 19505516 Free PMC article.
-
Actions of a histaminergic/peptidergic projection neuron on rhythmic motor patterns in the stomatogastric nervous system of the crab Cancer borealis.J Comp Neurol. 2004 Feb 2;469(2):153-69. doi: 10.1002/cne.11003. J Comp Neurol. 2004. PMID: 14694531 Free PMC article.
-
Frequency control of a slow oscillatory network by a fast rhythmic input: pyloric to gastric mill interactions in the crab stomatogastric nervous system.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998 Nov 16;860:226-38. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb09052.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998. PMID: 9928315 Review.
-
Neuropeptides are ubiquitous chemical mediators: Using the stomatogastric nervous system as a model system.J Exp Biol. 2001 Jun;204(Pt 12):2035-48. doi: 10.1242/jeb.204.12.2035. J Exp Biol. 2001. PMID: 11441046 Review.
Cited by
-
Function and Distribution of the Wamide Neuropeptide Superfamily in Metazoans.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020 May 28;11:344. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00344. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020. PMID: 32547494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Swim pacemaker response to bath applied neurotransmitters in the cubozoan Tripedalia cystophora.J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2013 Sep;199(9):785-97. doi: 10.1007/s00359-013-0839-1. Epub 2013 Jul 28. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23893247
-
Neuromodulation of neuronal circuits: back to the future.Neuron. 2012 Oct 4;76(1):1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.09.010. Neuron. 2012. PMID: 23040802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mass Spectrometric Profiling of Neuropeptides in Response to Copper Toxicity via Isobaric Tagging.Chem Res Toxicol. 2021 May 17;34(5):1329-1336. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.0c00521. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Chem Res Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33706502 Free PMC article.
-
Myoinhibitory peptide regulates feeding in the marine annelid Platynereis.Front Zool. 2015 Jan 7;12(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12983-014-0093-6. eCollection 2015. Front Zool. 2015. PMID: 25628752 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Audsley N, Matthews HJ, Price NR, Weaver RJ. Allatoregulatory peptides in Lepidoptera, structures, distribution and functions. J Insect Physiol. 2008;54(6):969–980. - PubMed
-
- Audsley N, Weaver RJ. Identification of neuropeptides from brains of larval Manduca sexta and Lacanobia oleracea using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry and post-source decay. Peptides. 2003;24(10):1465–1474. - PubMed
-
- Audsley N, Weaver RJ. Neuropeptides associated with the regulation of feeding in insects. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2009;162(1):93–104. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin DH, Graubard K. Distribution of fine neurites of stomatogastric neurons of the crab, Cancer borealis: evidence for a structured neuropil. J Comp Neurol. 1995;356:355–367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

