Central nervous system dysfunction in a mouse model of FA2H deficiency
- PMID: 21491498
- PMCID: PMC3094470
- DOI: 10.1002/glia.21172
Central nervous system dysfunction in a mouse model of FA2H deficiency
Abstract
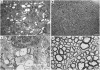
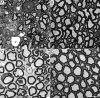
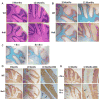
Fatty acid 2-hydroxylase (FA2H) is responsible for the synthesis of myelin galactolipids containing hydroxy fatty acid (hFA) as the N-acyl chain. Mutations in the FA2H gene cause leukodystrophy, spastic paraplegia, and neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. Using the Cre-lox system, we developed two types of mouse mutants, Fa2h(-/-) mice (Fa2h deleted in all cells by germline deletion) and Fa2h(flox/flox) Cnp1-Cre mice (Fa2h deleted only in oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells). We found significant demyelination, profound axonal loss, and abnormally enlarged axons in the CNS of Fa2h(-/-) mice at 12 months of age, while structure and function of peripheral nerves were largely unaffected. Fa2h(-/-) mice also exhibited histological and functional disruption in the cerebellum at 12 months of age. In a time course study, significant deterioration of cerebellar function was first detected at 7 months of age. Further behavioral assessments in water T-maze and Morris water maze tasks revealed significant deficits in spatial learning and memory at 4 months of age. These data suggest that various regions of the CNS are functionally compromised in young adult Fa2h(-/-) mice. The cerebellar deficits in 12-month-old Fa2h(flox/flox) Cnp1-Cre mice were indistinguishable from Fa2h(-/-) mice, indicating that these phenotypes likely stem from the lack of myelin hFA-galactolipids. In contrast, Fa2h(flox/flox) Cnp1-Cre mice did not show reduced performance in water maze tasks, indicating that oligodendrocytes are not involved in the learning and memory deficits found in Fa2h(-/-) mice. These findings provide the first evidence that FA2H has an important function outside of oligodendrocytes in the CNS.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Alderson NL, Maldonado EN, Kern MJ, Bhat NR, Hama H. FA2H-dependent fatty acid 2-hydroxylation in postnatal mouse brain. J Lipid Res. 2006;47:2772–80. - PubMed
-
- Alderson NL, Rembiesa BM, Walla MD, Bielawska A, Bielawski J, Hama H. The human FA2H gene encodes a fatty acid 2-hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:48562–8. - PubMed
-
- Bielawski J, Pierce JS, Snider J, Rembiesa B, Szulc ZM, Bielawska A. Comprehensive quantitative analysis of bioactive sphingolipids by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;579:443–67. - PubMed
-
- Boger HA, Middaugh LD, Huang P, Zaman V, Smith AC, Hoffer BJ, Tomac AC, Granholm AC. A partial GDNF depletion leads to earlier age-related deterioration of motor function and tyrosine hydroxylase expression in the substantia nigra. Exp Neurol. 2006;202:336–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG031675/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS056075/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS060807/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RR16434/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR017677/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- NS43174/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R03 NS056075/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY019320/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS043174/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR016434/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS060807/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AG31675/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- C06 RR015455/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR017677/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

