(5'S)-8,5'-cyclo-2'-deoxyguanosine is a strong block to replication, a potent pol V-dependent mutagenic lesion, and is inefficiently repaired in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 21491964
- PMCID: PMC3092667
- DOI: 10.1021/bi2004944
(5'S)-8,5'-cyclo-2'-deoxyguanosine is a strong block to replication, a potent pol V-dependent mutagenic lesion, and is inefficiently repaired in Escherichia coli
Abstract
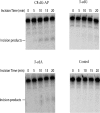
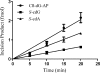
8,5'-Cyclopurines, making up an important class of ionizing radiation-induced tandem DNA damage, are repaired only by nucleotide excision repair (NER). They accumulate in NER-impaired cells, as in Cockayne syndrome group B and certain Xeroderma Pigmentosum patients. A plasmid containing (5'S)-8,5'-cyclo-2'-deoxyguanosine (S-cdG) was replicated in Escherichia coli with specific DNA polymerase knockouts. Viability was <1% in the wild-type strain, which increased to 5.5% with SOS. Viability decreased further in a pol II(-) strain, whereas it increased considerably in a pol IV(-) strain. Remarkably, no progeny was recovered from a pol V(-) strain, indicating that pol V is absolutely required for bypassing S-cdG. Progeny analyses indicated that S-cdG is significantly mutagenic, inducing ~34% mutation with SOS. Most mutations were S-cdG → A mutations, though S-cdG → T mutation and deletion of 5'C also occurred. Incisions of purified UvrABC nuclease on S-cdG, S-cdA, and C8-dG-AP on a duplex 51-mer showed that the incision rates are C8-dG-AP > S-cdA > S-cdG. In summary, S-cdG is a major block to DNA replication, highly mutagenic, and repaired slowly in E. coli.
Figures
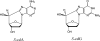
References
-
- Chatgilialoglu C.; Ferreri C.; Terzidis M. A. (2011) Chem. Soc. Rev. 40, 1368–1382. - PubMed
-
- Jaruga P.; Birincioglu M.; Rodriguez H.; Dizdaroglu M. (2002) Biochemistry 41, 3703–3711. - PubMed
-
- Jaruga P.; Dizdaroglu M. (2008) DNA Repair 7, 1413–1425. - PubMed
-
- Keck K. (1968) Z. Naturforsch., B 23, 1034–1043. - PubMed
-
- Brooks P. J.; Wise D. S.; Berry D. A.; Kosmoski J. V.; Smerdon M. J.; Somers R. L.; Mackie H.; Spoonde A. Y.; Ackerman E. J.; Coleman K.; Tarone R. E.; Robbins J. H. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 22355–22362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

