Protein synthesis of the pro-inflammatory S100A8/A9 complex in plasmacytoid dendritic cells and cell surface S100A8/A9 on leukocyte subpopulations in systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 21492422
- PMCID: PMC3132055
- DOI: 10.1186/ar3314
Protein synthesis of the pro-inflammatory S100A8/A9 complex in plasmacytoid dendritic cells and cell surface S100A8/A9 on leukocyte subpopulations in systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Introduction: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease with chronic or episodic inflammation in many different organ systems, activation of leukocytes and production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. The heterodimer of the cytosolic calcium-binding proteins S100A8 and S100A9 (S100A8/A9) is secreted by activated polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) and monocytes and serves as a serum marker for several inflammatory diseases. Furthermore, S100A8 and S100A9 have many pro-inflammatory properties such as binding to Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). In this study we investigated if aberrant cell surface S100A8/A9 could be seen in SLE and if plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) could synthesize S100A8/A9.
Methods: Flow cytometry, confocal microscopy and real-time PCR of flow cytometry-sorted cells were used to measure cell surface S100A8/A9, intracellular S100A8/A9 and mRNA levels of S100A8 and S100A9, respectively.
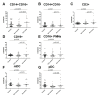
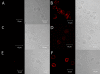
Results: Cell surface S100A8/A9 was detected on all leukocyte subpopulations investigated except for T cells. By confocal microscopy, real-time PCR and stimulation assays, we could demonstrate that pDCs, monocytes and PMNs could synthesize S100A8/A9. Furthermore, pDC cell surface S100A8/A9 was higher in patients with active disease as compared to patients with inactive disease. Upon immune complex stimulation, pDCs up-regulated the cell surface S100A8/A9. SLE patients had also increased serum levels of S100A8/A9.
Conclusions: Patients with SLE had increased cell surface S100A8/A9, which could be important in amplification and persistence of inflammation. Importantly, pDCs were able to synthesize S100A8/A9 proteins and up-regulate the cell surface expression upon immune complex-stimulation. Thus, S100A8/A9 may be a potent target for treatment of inflammatory diseases such as SLE.
Figures

References
-
- Manson JJ, Isenberg DA. The pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Neth J Med. 2003;61:343–346. - PubMed
-
- Wei C, Anolik J, Cappione A, Zheng B, Pugh-Bernard A, Brooks J, Lee EH, Milner EC, Sanz I. A new population of cells lacking expression of CD27 represents a notable component of the B cell memory compartment in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 2007;178:6624–6633. - PubMed
-
- Odendahl M, Jacobi A, Hansen A, Feist E, Hiepe F, Burmester GR, Lipsky PE, Radbruch A, Dorner T. Disturbed peripheral B lymphocyte homeostasis in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol. 2000;165:5970–5979. - PubMed
-
- Viallard JF, Bloch-Michel C, Neau-Cransac M, Taupin JL, Garrigue S, Miossec V, Mercie P, Pellegrin JL, Moreau JF. HLA-DR expression on lymphocyte subsets as a marker of disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Immunol. 2001;125:485–491. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01623.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

