A research strategy case study of alcohol and drug prevention by non-governmental organizations in Sweden 2003-2009
- PMID: 21492442
- PMCID: PMC3102619
- DOI: 10.1186/1747-597X-6-8
A research strategy case study of alcohol and drug prevention by non-governmental organizations in Sweden 2003-2009
Abstract
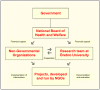
Background: Alcohol and drug prevention is high on the public health agenda in many countries. An increasing trend is the call for evidence-based practice. In Sweden in 2002 an innovative project portfolio including an integrated research and competence-building strategy for non-governmental organisations (NGOs) was designed by the National Board of Health and Welfare (NBHW). This research strategy case study is based on this initiative.
Methods: The embedded case study includes 135 projects in 69 organisations and 14 in-depth process or effect studies. The data in the case study has been compiled using multiple methods - administrative data; interviews and questionnaires to project leaders; focus group discussions and seminars; direct and participatory observations, interviews, and documentation of implementation; consultations with the NBHW and the NGOs; and a literature review. Annual reports have been submitted each year and three bi-national conferences Reflections on preventions have been held.
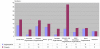
Results: A broad range of organisations have been included in the NBHW project portfolio. A minority of the project were run by Alcohol or drug organisations, while a majority has children or adolescents as target groups. In order to develop a trustful partnership between practitioners, national agencies and researchers a series of measures were developed and implemented: meeting with project leaders, project dialogues and consultations, competence strengthening, support to documentation, in-depth studies and national conferences. A common element was that the projects were program-driven and not research-driven interventions. The role of researchers-as-technical advisors was suitable for the fostering of a trustful partnership for research and development. The independence of the NGOs was regarded as important for the momentum in the project implementation. The research strategy also includes elements of participatory research.
Conclusions: This research strategy case study shows that it is possible to integrate research into alcohol and drug prevention programs run by NGOs, and thereby contribute to a more evidence-based practice. A core element is developing a trustful partnership between the researchers and the organisations. Moreover, the funding agency must acknowledge the importance of knowledge development and allocating resources to research groups that is capable of cooperating with practitioners and NGOs.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Design and implementation of RESCUR in Sweden for promoting resilience in children: a study protocol.BMC Public Health. 2018 Nov 12;18(1):1250. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-6145-7. BMC Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30419888 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Shifting participatory approach when ideology meets reality: a grounded theory study based on project leaders' experiences with peer-led sex education programs for and by persons with intellectual disabilities and/or autism.Reprod Health. 2025 Mar 6;22(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12978-025-01975-6. Reprod Health. 2025. PMID: 40050908 Free PMC article.
-
HIV prevention nongovernmental organizations in Central and Eastern Europe: programs, resources and challenges.Cent Eur J Public Health. 2004 Mar;12(1):12-8. Cent Eur J Public Health. 2004. PMID: 15068200
-
A review of reviews on principles, strategies, outcomes and impacts of research partnerships approaches: a first step in synthesising the research partnership literature.Health Res Policy Syst. 2020 May 25;18(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12961-020-0544-9. Health Res Policy Syst. 2020. PMID: 32450919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Community health outreach program of the Chad-Cameroon petroleum development and pipeline project.Clin Occup Environ Med. 2004 Feb;4(1):9-26. doi: 10.1016/j.coem.2003.09.004. Clin Occup Environ Med. 2004. PMID: 15043361 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the effectiveness of the SMART contract-signing strategy in reducing the growth of Swedish Adolescents' substance use and problem behaviors.BMC Public Health. 2016 Jun 22;16:519. doi: 10.1186/s12889-016-3131-9. BMC Public Health. 2016. PMID: 27333865 Free PMC article.
-
Building Public Health Capacity through Organizational Change in the Sport System: A Multiple-Case Study within Australian Gymnastics.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jun 22;18(13):6726. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18136726. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34206499 Free PMC article.
-
Effects on alcohol use of a Swedish school-based prevention program for early adolescents: a longitudinal study.BMC Public Health. 2017 Jan 3;17(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12889-016-3947-3. BMC Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28049504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Handbook for action to reduce alcohol-related harm. Copenhagen: World Health Organization; 2009.
-
- Davies JK, Macdonald G, (Eds) Quality, Evidence and Effectiveness in Health Promotion. London: Routledge; 1998.
-
- Eriksson C. Learning and knowledge-production for public health - a review of approaches to evidence-based public health. Scandinavian Journal of Public Health. 2000;28:298–308. - PubMed
-
- Gomm R, Davies C, (Eds) Using Evidence in Health and Social Care. London: Sage; 2000.
-
- Oakley A. Experiment in Knowing. Gender and method in the social sciences. Cambridge: Polity Press; 2000.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

