A high-density transcript linkage map with 1,845 expressed genes positioned by microarray-based Single Feature Polymorphisms (SFP) in Eucalyptus
- PMID: 21492453
- PMCID: PMC3090358
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-189
A high-density transcript linkage map with 1,845 expressed genes positioned by microarray-based Single Feature Polymorphisms (SFP) in Eucalyptus
Abstract
Background: Technological advances are progressively increasing the application of genomics to a wider array of economically and ecologically important species. High-density maps enriched for transcribed genes facilitate the discovery of connections between genes and phenotypes. We report the construction of a high-density linkage map of expressed genes for the heterozygous genome of Eucalyptus using Single Feature Polymorphism (SFP) markers.
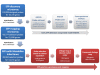
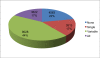
Results: SFP discovery and mapping was achieved using pseudo-testcross screening and selective mapping to simultaneously optimize linkage mapping and microarray costs. SFP genotyping was carried out by hybridizing complementary RNA prepared from 4.5 year-old trees xylem to an SFP array containing 103,000 25-mer oligonucleotide probes representing 20,726 unigenes derived from a modest size expressed sequence tags collection. An SFP-mapping microarray with 43,777 selected candidate SFP probes representing 15,698 genes was subsequently designed and used to genotype SFPs in a larger subset of the segregating population drawn by selective mapping. A total of 1,845 genes were mapped, with 884 of them ordered with high likelihood support on a framework map anchored to 180 microsatellites with average density of 1.2 cM. Using more probes per unigene increased by two-fold the likelihood of detecting segregating SFPs eventually resulting in more genes mapped. In silico validation showed that 87% of the SFPs map to the expected location on the 4.5X draft sequence of the Eucalyptus grandis genome.
Conclusions: The Eucalyptus 1,845 gene map is the most highly enriched map for transcriptional information for any forest tree species to date. It represents a major improvement on the number of genes previously positioned on Eucalyptus maps and provides an initial glimpse at the gene space for this global tree genome. A general protocol is proposed to build high-density transcript linkage maps in less characterized plant species by SFP genotyping with a concurrent objective of reducing microarray costs. HIgh-density gene-rich maps represent a powerful resource to assist gene discovery endeavors when used in combination with QTL and association mapping and should be especially valuable to assist the assembly of reference genome sequences soon to come for several plant and animal species.
Figures

References
-
- Bernardo R. Molecular markers and selection for complex traits in plants: Learning from the last 20 years. Crop Science. 2008;48(5):1649–1664. doi: 10.2135/cropsci2008.03.0131. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

