Facilitation of the acoustic startle reflex by ponto-geniculo-occipital waves: effects of PCPA
- PMID: 2149298
- PMCID: PMC9148914
- DOI: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91765-9
Facilitation of the acoustic startle reflex by ponto-geniculo-occipital waves: effects of PCPA
Abstract
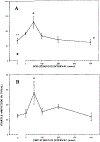
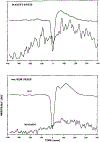
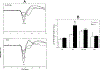
The relationship between ponto-geniculo-occipital (PGO) waves and motor activity during waking and non-rapid eye movement (non-REM) sleep stages was studied in cats treated with the serotonin synthesis inhibitor p-chlorophenylalanine (PCPA). PGO waves appeared in waking after daily treatment with PCPA. The magnitude of the acoustic startle elicited in the absence of prior PGO waves was increased (by a mean of 555%) by the PCPA treatment as compared to that of the pre-drug level. When startle-eliciting stimuli were presented shortly after the occurrence of the PGO wave, the response amplitude was further enhanced as compared to that of the baseline startle. The effect was maximal 50 ms following the peak of the PGO wave (average 192% of the baseline level), with return to the baseline startle level within 200 ms. A similar effect could also be seen with waking eye-movement potentials (EMPs) in drug-naive animals. Over half of the spontaneous PGO waves were found to be preceded or followed by discrete head-body movements. After PCPA, the amplitude of auditory-evoked LGN PGO waves increased during quiet waking (QW) while those in non-REM and REM sleep states did not change. It was concluded that serotonergic systems produce a tonic suppression of startle response and PGO amplitude in waking. PGO spikes in waking are associated with a phasic facilitation of the sensorimotor mechanisms involved in startle.
Figures
References
-
- Carlton EL. and Advokat C, Attenuated habituation due to parachlorophenylalanine, Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav, 1 (1973) 657–663. - PubMed
-
- Chase MH and Morales FR, Subthreshold excitatory activity and motoneuron discharge during REM periods of active sleep, Science, 221 (1983) 1195–1198. - PubMed
-
- Conner RL, Stolk JM, Barchas JD and Levine S, Parachlorophenylalanine and habituation to repetitive auditory startle stimuli in rats, Physiol. Behav, 5 (1970) 1215–1219. - PubMed
-
- Davis M and Sheard MH, Habituation and sensitization of the rat startle response: effects of raphe lesions, Physiol. Behav, 12 (1974) 425–431. - PubMed
-
- Davis M, Astrachan DI and Kaas E, Excitatory and inhibitory effects of serotonin on sensorimotor reactivity measured with acoustic startle, Science, 209 (1980) 521–523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

