Estrogen receptor β induces antiinflammatory and antitumorigenic networks in colon cancer cells
- PMID: 21493669
- PMCID: PMC5417254
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2010-0452
Estrogen receptor β induces antiinflammatory and antitumorigenic networks in colon cancer cells
Abstract
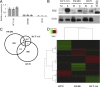
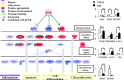
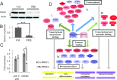
Several studies suggest estrogen to be protective against the development of colon cancer. Estrogen receptor β (ERβ) is the predominant estrogen receptor expressed in colorectal epithelium and is the main candidate to mediate the protective effects. We have previously shown that expression of ERβ reduces growth of colorectal cancer in xenografts. Little is known of the actions of ERβ and its effect on gene transcription in colon cancers. To dissect the processes that ERβ mediates and to investigate cell-specific mechanisms, we reexpressed ERβ in three colorectal cancer cell lines (SW480, HT29, and HCT-116) and conducted genome-wide expression studies in combination with gene-pathway analyses and cross-correlation to ERβ-chromatin-binding sites. Although induced gene regulation was cell specific, overrepresentation analysis of functional classes indicated that the same biological themes, including apoptosis, cell differentiation, and regulation of the cell cycle, were affected in all three cell lines. Novel findings include a strong ERβ-mediated down-regulation of IL-6 and downstream networks with significant implications for inflammatory mechanisms involved in colon carcinogenesis. We also discovered cross talk between the suggested nuclear receptor coregulator PROX1 and ERβ, demonstrating that ERβ both regulates and shares target genes with PROX1. The influence of ERβ on apoptosis was further explored using functional studies, which suggested an increased DNA-repair capacity. We conclude that reexpression of ERβ induces transcriptome changes that, through several parallel pathways, converge into antitumorigenic capabilities in all three cell lines. We propose that enhancing ERβ action has potential as a novel therapeutic approach for prevention and/or treatment of colon cancer.
Figures

References
-
- Grodstein F , Newcomb PA , Stampfer MJ. 1999. Postmenopausal hormone therapy and the risk of colorectal cancer: a review and meta-analysis. Am J Med 106:574–582 - PubMed
-
- Newcomb PA , Zheng Y , Chia VM , Morimoto LM , Doria-Rose VP , Templeton A , Thibodeau SN , Potter JD. 2007. Estrogen plus progestin use, microsatellite instability, and the risk of colorectal cancer in women. Cancer Res 67:7534–7539 - PubMed
-
- Park BW , Kim KS , Heo MK , Ko SS , Hong SW , Yang WI , Kim JH , Kim GE , Lee KS. 2003. Expression of estrogen receptor-β in normal mammary and tumor tissues: is it protective in breast carcinogenesis? Breast Cancer Res Treat 80:79–85 - PubMed
-
- Pasquali D , Staibano S , Prezioso D , Franco R , Esposito D , Notaro A , De Rosa G , Bellastella A , Sinisi AA. 2001. Estrogen receptor β expression in human prostate tissue. Mol Cell Endocrinol 178:47–50 - PubMed
-
- Rutherford T , Brown WD , Sapi E , Aschkenazi S , Muñoz A , Mor G. 2000. Absence of estrogen receptor-beta expression in metastatic ovarian cancer. Obstet Gynecol 96:417–421 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

