Alanine 32 in PilA is important for PilA stability and type IV pili function in Myxococcus xanthus
- PMID: 21493683
- PMCID: PMC3167889
- DOI: 10.1099/mic.0.049684-0
Alanine 32 in PilA is important for PilA stability and type IV pili function in Myxococcus xanthus
Abstract
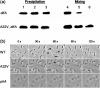
Type IV pili (TFP) are membrane-anchored filaments with a number of important biological functions. In the model organism Myxococcus xanthus, TFP act as molecular engines that power social (S) motility through cycles of extension and retraction. TFP filaments consist of several thousand copies of a protein called PilA or pilin. PilA contains an N-terminal α-helix essential for TFP assembly and a C-terminal globular domain important for its activity. The role of the PilA sequence and its structure-function relationship in TFP-dependent S motility remain active areas of research. In this study, we identified an M. xanthus PilA mutant carrying an alanine to valine substitution at position 32 in the α-helix, which produced structurally intact but retraction-defective TFP. Characterization of this mutant and additional single-residue variants at this position in PilA demonstrated the critical role of alanine 32 in PilA stability, TFP assembly and retraction.
Figures



References
-
- Aas F. E., Winther-Larsen H. C., Wolfgang M., Frye S., Løvold C., Roos N., van Putten J. P., Koomey M. (2007). Substitutions in the N-terminal alpha helical spine of Neisseria gonorrhoeae pilin affect type IV pilus assembly, dynamics and associated functions. Mol Microbiol 63, 69–85. 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05482.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

