Icodextrin increases technique survival rate in peritoneal dialysis patients with diabetic nephropathy by improving body fluid management: a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 21493740
- PMCID: PMC3109930
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.10041110
Icodextrin increases technique survival rate in peritoneal dialysis patients with diabetic nephropathy by improving body fluid management: a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background and objectives: There are still controversies whether peritoneal dialysis (PD) with icodextrin preserves residual renal and peritoneal membrane functions in patients with diabetes. However, there are no randomized controlled and long-term clinical trials in newly started PD patients with diabetic nephropathy.
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Forty-one patients with diabetic nephropathy with ESRD were enrolled and randomly assigned to the glucose group (GLU) treated with 8 L of 1.5% or 2.5% glucose or an icodextrin group (ICO) treated with 1.5 or 2.0 L of 7.5% icodextrin-containing solutions. Technique failure, body fluid management, glucose and lipid metabolism, and residual renal and peritoneal functions and were evaluated over 2 years.
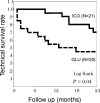
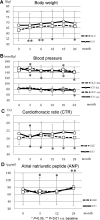
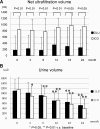
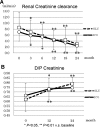
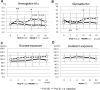
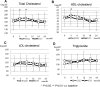
Results: The technique survival rate was 71.4% in ICO and 45.0% in GLU, with most of the technique failure due to volume overload. ICO showed significantly better cumulative technique survival. Net ultrafiltration volume was significantly higher in ICO throughout the study period. There were no beneficial effects of icodextrin on hemoglobin A1c, glycoalbumin, and lipid profile at 24 months. Urine volume and residual renal function declined faster in ICO, but there were no significant differences between the two groups. For peritoneal function, no differences were observed in dialysis-to-plasma creatinine ratios during the observation.
Conclusions: In PD therapy for diabetic nephropathy, the use of icodextrin-containing solutions has a beneficial effect on technique survival, but there are no apparent benefits or disadvantages in residual renal and peritoneal functions compared with conventional PD with glucose solution.
Figures
References
-
- Kuriyama S: Peritoneal dialysis in patients with diabetes: Are the benefits greater than the disadvantages? Perit Dial Int 27[Suppl 2]: S190–S195, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Masakane I, Tsubakihara Y, Akiba T, Watanabe Y, Iseki K: The most recent trends of peritoneal dialysis in Japan. Perit Dial Int 28[Suppl 3]: S27–S31, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Mistry CD, Gokal R, Peers E: A randomized multicenter clinical trial comparing isosmolar icodextrin with hyperosmolar glucose solutions in CAPD. MIDAS Study Group. Multicenter Investigation of Icodextrin in Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis. Kidney Int 46: 496–503, 1994 - PubMed
-
- Mistry CD, Mallick NP, Gokal R: Ultrafiltration with an isosmotic solution during long peritoneal dialysis exchanges. Lancet 2: 178–182, 1987 - PubMed
-
- Frampton JE, Plosker GL: Icodextrin: A review of its use in peritoneal dialysis. Drugs 63: 2079–2105, 2003 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

