MRI using ferumoxytol improves the visualization of central nervous system vascular malformations
- PMID: 21493906
- PMCID: PMC3412426
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.607994
MRI using ferumoxytol improves the visualization of central nervous system vascular malformations
Abstract
Background and purpose: Central nervous system vascular malformations (VMs) result from abnormal vasculo- and/or angiogenesis. Cavernomas and arteriovenous malformations are also sites of active inflammation. The aim of this study was to determine whether MRI detection of VMs can be improved by administration of ferumoxytol iron oxide nanoparticle, which acts as a blood pool agent at early time points and an inflammatory marker when taken up by tissue macrophages.
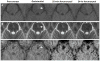
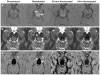
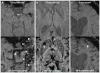
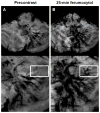
Methods: Nineteen patients (11 men, 8 women; mean age, 47.5 years) with central nervous system VMs underwent 3-T MRI both with gadoteridol and ferumoxytol. The ferumoxytol-induced signal changes on the T1-, T2-, and susceptibility-weighted images were analyzed at 25 minutes (range, 21 to 30 minutes) and 24 hours (range, 22 to 27 hours).
Results: Thirty-five lesions (capillary telangiectasia, n=6; cavernoma, n=21; developmental venous anomaly, n=7; arteriovenous malformation, n=1) were seen on the pre- and postgadoteridol images. The postferumoxytol susceptibility-weighted sequences revealed 5 additional VMs (3 capillary telangiectasias, 2 cavernomas) and demonstrated further tributary veins in all patients with developmental venous anomalies. The 24-hour T1 and T2 ferumoxytol-related signal abnormalities were inconsistent among patients and within VM types. No additional area of T1 or T2 enhancement was noted with ferumoxytol compared with gadoteridol in any lesion.
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that the blood pool agent ferumoxytol provides important information about the number and true extent of VMs on the susceptibility-weighted MRI. The use of ferumoxytol as a macrophage imaging agent in the visualization of inflammatory cells within and around the lesions warrants further investigation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Brown RD, Jr, Flemming KD, Meyer FB, Cloft HJ, Pollock BE, Link ML. Natural history, evaluation, and management of intracranial vascular malformations. Mayo Clin Proc. 2005;80:269–281. Review. - PubMed
-
- Krings T, Lasjaunias PL, Hans FJ, Mull M, Nijenhuis RJ, Alvarez H, Backes WH, Reinges MH, Rodesch G, Gilsbach JM, Thron AK. Imaging in spinal vascular disease. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2007;17:57–72. Review. - PubMed
-
- Gault J, Sarin H, Awadallah NA, Shenkar R, Awad IA. Pathobiology of human cerebrovascular malformations: basic mechanisms and clinical relevance. Neurosurgery. 2004;55:1–16. discussion 16–17. Review. - PubMed
-
- Sehgal V, Delproposto Z, Haacke EM, Tong KA, Wycliffe N, Kido DK, Xu Y, Neelavalli J, Haddar D, Reichenbach JR. Clinical applications of neuroimaging with susceptibility-weighted imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2005;22:439–450. Review. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

