Minimal atrophy of the entorhinal cortex and hippocampus: progression of cognitive impairment
- PMID: 21494034
- PMCID: PMC3085034
- DOI: 10.1159/000324711
Minimal atrophy of the entorhinal cortex and hippocampus: progression of cognitive impairment
Abstract
Background: In Alzheimer's disease, neurodegenerative atrophy progresses from the entorhinal cortex (ERC) to the hippocampus (HP), limbic system and neocortex. The significance of very mild atrophy of the ERC and HP on MRI scans among elderly subjects is unknown.
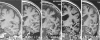
Methods: A validated visual rating system on coronal MRI scans was used to identify no atrophy of the HP or ERC (HP(0); ERC(0)), or minimal atrophy of the HP or ERC (HP(ma); ERC(ma)), among 414 participants. Subjects fell into the following groups: (1) ERC(0)/HP(0), (2) ERC(ma)/HP(0), (3) ERC(0)/HP(ma), and (4) ERC(ma)/HP(ma). HP volume was independently measured using volumetric methods.
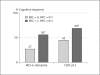
Results: In comparison to ERC(0)/HP(0) subjects, those with ERC(0)/HP(ma) had impairment on 1 memory test, ERC(ma)/HP(0) subjects had impairment on 2 memory tests and the Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE), while ERC(ma)/HP(ma) subjects had impairment on 3 memory tests, the MMSE and Clinical Dementia Rating. Progression rates of cognitive and functional impairment were significantly greater among subjects with ERC(ma).
Conclusion: Minimal atrophy of the ERC results in greater impairment than minimal atrophy of the HP, and the combination is additive when measured by cognitive and functional tests. Rates of progression to greater impairment were higher among ERC(ma) subjects.
Copyright © 2011 S. Karger AG, Basel.
Figures
References
-
- Riemenschneider M, Lautenschlager N, Wagenpfeil S, Diehl J, Drzezga A, Kurz A. Cerebrospinal fluid tau and beta-amyloid 42 proteins identify Alzheimer disease in subjects with mild cognitive impairment. Arch Neurol. 2002;59:1729–1734. - PubMed
-
- Mattsson N, Zetterberg H, Hansson O, Andreasen N, Parnetti L, Jonsson M, Herukka SK, van der Flier WM, Blankenstein MA, Ewers M, Rich K, Kaiser E, Verbeek M, Tsolaki M, Mulugeta E, Rosén E, Aarsland D, Visser PJ, Schröder J, Marcusson J, de Leon M, Hampel H, Scheltens P, Pirttilä T, Wallin A, Jönhagen ME, Minthon L, Winblad KB, Blennow CSF Biomarkers and incipient Alzheimer disease in patients with mild cognitive impairment. JAMA. 2009;302:385–393. - PubMed
-
- Klunk WE, Engler H, Nordberg A, Wang Y, Blomqvist G, Holt DP, Bergström M, Savitcheva I, Huang GF, Estrada S, Ausén B, Debnath ML, Barletta J, Price JC, Sandell J, Lopresti BJ, Wall A, Koivisto P, Antoni G, Mathis CA, Långström B. Imaging brain amyloid in Alzheimer's disease with Pittsburgh Compound-B. Ann Neurol. 2004;55:306–319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

