A case of pedicle screw loosening treated by modified transpedicular screw augmentation with polymethylmethacrylate
- PMID: 21494370
- PMCID: PMC3070902
- DOI: 10.3340/jkns.2011.49.1.75
A case of pedicle screw loosening treated by modified transpedicular screw augmentation with polymethylmethacrylate
Abstract
We report a case of pedicle screw loosening treated by modified transpedicular screw augmentation technique using polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA), which used the anchoring effect of hardened PMMA. A 56-year-old man who had an L3/4/5 fusion operation 3 years ago complained of continuous low back pain after this operation. The computerized tomography showed a radiolucent halo around the pedicle screw at L5. We augmented the L5 pedicle screw with modified pedicle screw augmentation technique using PMMA and performed an L3/4/5 pedicle screw fixation without hook or operation field extension. This modified technique is a kind of transpedicular stiffness augmentation using PMMA for the dead space around the loosed screw. After filling the dead space with 1-2 cc of PMMA, we inserted a small screw. Once the PMMA hardened, we removed the small screw and inserted a thicker screw along the existing screw threading to improve the pedicle screws' pullout strength. At 10 months' follow-up, x-ray showed strong fusion of L3/4/5. The visual analogue scale (VAS) of his back pain was improved from 9 to 5. This modified transpedicular screw augmentation with PMMA using anchoring effect is a simple and effective surgical technique for pedicle screw loosening. However, clinical analyses of long-term follow-up and biomechanical studies are needed.
Keywords: Instrument failure; Osteoporosis; PMMA; Pedicle screw loosening; Pseudoarthrosis; Surgical technique.
Figures
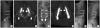

References
-
- Aydogan M, Ozturk C, Karatoprak O, Tezer M, Aksu N, Hamzaoglu A. The pedicle screw fixation with vertebroplasty augmentation in the surgical treatment of the severe osteoporotic spines. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2009;22:444–447. - PubMed
-
- Bullmann V, Liljenqvist UR, Schmidt C, Schulte TL. [posterior operative correction of idiopathic scoliosis. Value of pedicle screws versus hooks] Orthopade. 2009;38:198–200. 202–204. - PubMed
-
- Burval DJ, McLain RF, Milks R, Inceoglu S. Primary pedicle screw augmentation in osteoporotic lumbar vertebrae : biomechanical analysis of pedicle fixation strength. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2007;32:1077–1083. - PubMed
-
- Chang MC, Liu CL, Chen TH. Polymethylmethacrylate augmentation of pedicle screw for osteoporotic spinal surgery : a novel technique. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2008;33:E317–E324. - PubMed
-
- Frankel BM, Jones T, Wang C. Segmental polymethylmethacrylate-augmented pedicle screw fixation in patients with bone softening caused by osteoporosis and metastatic tumor involvement : a clinical evaluation. Neurosurgery. 2007;61:531–537. discussion 537-538. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

