Dietary Aloe Improves Insulin Sensitivity via the Suppression of Obesity-induced Inflammation in Obese Mice
- PMID: 21494375
- PMCID: PMC3072676
- DOI: 10.4110/in.2011.11.1.59
Dietary Aloe Improves Insulin Sensitivity via the Suppression of Obesity-induced Inflammation in Obese Mice
Abstract
Background: Insulin resistance is an integral feature of metabolic syndromes, including obesity, hyperglycemia, and hyperlipidemia. In this study, we evaluated whether the aloe component could reduce obesity-induced inflammation and the occurrence of metabolic disorders such as blood glucose and insulin resistance.
Methods: Male C57BL/6 obese mice fed a high-fat diet for 54 days received a supplement of aloe formula (PAG, ALS, Aloe QDM, and Aloe QDM complex) or pioglitazone (PGZ) and were compared with unsupplemented controls (high-fat diet; HFD) or mice fed a regular diet (RD). RT-PCR and western blot analysis were used to quantify the expression of obesity-induced inflammation.
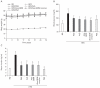
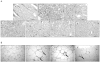
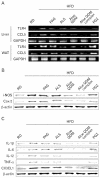
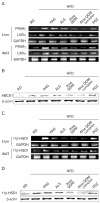
Results: Aloe QDM lowered fasting blood glucose and plasma insulin compared with HFD. Obesity-induced inflammatory cytokine (IL-1β, -6, -12, TNF-α) and chemokine (CX3CL1, CCL5) mRNA and protein were decreased markedly, as was macrophage infiltration and hepatic triglycerides by Aloe QDM. At the same time, Aloe QDM decreased the mRNA and protein of PPARγ/LXRα and 11β-HSD1 both in the liver and WAT.
Conclusion: Dietary aloe formula reduces obesity-induced glucose tolerance not only by suppressing inflammatory responses but also by inducing anti-inflammatory cytokines in the WAT and liver, both of which are important peripheral tissues affecting insulin resistance. The effect of Aloe QDM complex in the WAT and liver are related to its dual action on PPARγ and 11β-HSD1 expression and its use as a nutritional intervention against T2D and obesity-related inflammation is suggested.
Keywords: Aloe QDM complex; Insulin sensitivity; Obesity-induced inflammation; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The author have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Pickup JC, Crook MA. Is type II diabetes mellitus a disease of the innate immune system? Diabetologia. 1998;41:1241–1248. - PubMed
-
- Grimble RF. Inflammatory status and insulin resistance. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2002;5:551–559. - PubMed
-
- Uysal KT, Wiesbrock SM, Marino MW, Hotamisligil GS. Protection from obesity-induced insulin resistance in mice lacking TNF-alpha function. Nature. 1997;389:610–614. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

