Five methods of breast volume measurement: a comparative study of measurements of specimen volume in 30 mastectomy cases
- PMID: 21494401
- PMCID: PMC3076010
- DOI: 10.4137/BCBCR.S6128
Five methods of breast volume measurement: a comparative study of measurements of specimen volume in 30 mastectomy cases
Abstract
Background: To compare breast volume measurement techniques in terms of accuracy, convenience, and cost.
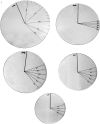
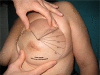
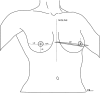
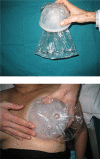
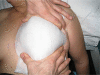
Methods: Breast volumes of 30 patients who were scheduled to undergo total mastectomy surgery were measured preoperatively by using five different methods (mammography, anatomic [anthropometric], thermoplastic casting, the Archimedes procedure, and the Grossman-Roudner device). Specimen volume after total mastectomy was measured in each patient with the water displacement method (Archimedes). The results were compared statistically with the values obtained by the five different methods.
Results: The mean mastectomy specimen volume was 623.5 (range 150-1490) mL. The breast volume values were established to be 615.7 mL (r = 0.997) with the mammographic method, 645.4 mL (r = 0.975) with the anthropometric method, 565.8 mL (r = 0.934) with the Grossman-Roudner device, 583.2 mL (r = 0.989) with the Archimedes procedure, and 544.7 mL (r = 0.94) with the casting technique. Examination of r values revealed that the most accurate method was mammography for all volume ranges, followed by the Archimedes method.
Conclusion: The present study demonstrated that the most accurate method of breast volume measurement is mammography, followed by the Archimedes method. However, when patient comfort, ease of application, and cost were taken into consideration, the Grossman-Roudner device and anatomic measurement were relatively less expensive, and easier methods with an acceptable degree of accuracy.
Keywords: breast density; macromastia; mammography-negativity; oncoplastic surgery; reduction mammaplasty.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The cost effectiveness of three different measures of breast volume.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2006 Jan-Feb;30(1):16-20. doi: 10.1007/s00266-004-0105-6. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2006. PMID: 16411159
-
Breast Volume Measurement by Recycling the Data Obtained From 2 Routine Modalities, Mammography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging.Eplasty. 2017 Dec 20;17:e39. eCollection 2017. Eplasty. 2017. PMID: 29308107 Free PMC article.
-
Breast volume assessment: comparing five different techniques.Breast. 2001 Apr;10(2):117-23. doi: 10.1054/brst.2000.0196. Breast. 2001. PMID: 14965570
-
Oncoplastic breast conserving surgery: Volume replacement vs. volume displacement.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2016 Jul;42(7):926-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2016.02.248. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26988623 Review.
-
[Methods and importance of volume measurement in reconstructive and aesthetic breast surgery].Orv Hetil. 2014 Mar 16;155(11):407-13. doi: 10.1556/OH.2014.29810. Orv Hetil. 2014. PMID: 24613775 Review. Hungarian.
Cited by
-
Influence of Weight Loss on Volumetric Change in Contralateral Breast During 2-Stage Breast Reconstruction.Eplasty. 2018 Sep 27;18:e27. eCollection 2018. Eplasty. 2018. PMID: 30333899 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of 3D imaging to guide implant selection in immediate breast reconstruction.JPRAS Open. 2021 Oct 29;31:50-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jpra.2021.10.007. eCollection 2022 Mar. JPRAS Open. 2021. PMID: 34934793 Free PMC article.
-
Engineered Fat Graft Enhanced with Adipose-Derived Stromal Vascular Fraction Cells for Regenerative Medicine: Clinical, Histological and Instrumental Evaluation in Breast Reconstruction.J Clin Med. 2019 Apr 12;8(4):504. doi: 10.3390/jcm8040504. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31013744 Free PMC article.
-
In-vivo quantification of human breast deformation associated with the position change from supine to upright.Med Eng Phys. 2015 Jan;37(1):13-22. doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2014.09.016. Epub 2014 Oct 19. Med Eng Phys. 2015. PMID: 25456398 Free PMC article.
-
A prospective study of breast anthropomorphic measurements, volume and ptosis in 605 Asian patients with breast cancer or benign breast disease.PLoS One. 2017 Feb 13;12(2):e0172122. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172122. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28192525 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kayar R, Catal H. Macromastia and breast cancer. Izmir Tepecik Hstn Derg. 2007;17:121–30.
-
- Brown RW, Cheng Y, Kurtay M. A formula for surgical modifications of the breast. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000;106:1342–5. - PubMed
-
- Cochrane RA, Valasiadou P, Wilson ARM, Al-Chazal SK, Mcmillan RD. Cosmesis and satisfaction after breast-conserving surgery correlates with the percentage of breast volume excised. Br J Surg. 2003;90:1505–9. - PubMed
-
- Bullstrode NW, Shrotria S. Prediction of cosmetic outcome following conservative breast surgery using breast volume measurements. Breast. 2001;10:124–6. - PubMed
-
- Kovacs L, Eder M, Hollweck R, et al. Comparison between breast volume measurement using 3 D surface imaging and classical techniques. Breast. 2007;16:137–45. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

