Ultra-fast and sensitive detection of non-typhoidal Salmonella using microwave-accelerated metal-enhanced fluorescence ("MAMEF")
- PMID: 21494634
- PMCID: PMC3073000
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018700
Ultra-fast and sensitive detection of non-typhoidal Salmonella using microwave-accelerated metal-enhanced fluorescence ("MAMEF")
Abstract
Certain serovars of Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica cause invasive disease (e.g., enteric fever, bacteremia, septicemia, meningitis, etc.) in humans and constitute a global public health problem. A rapid, sensitive diagnostic test is needed to allow prompt initiation of therapy in individual patients and for measuring disease burden at the population level. An innovative and promising new rapid diagnostic technique is microwave-accelerated metal-enhanced fluorescence (MAMEF). We have adapted this assay platform to detect the chromosomal oriC locus common to all Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovars. We have shown efficient lysis of biologically relevant concentrations of Salmonella spp. suspended in bacteriological media using microwave-induced lysis. Following lysis and DNA release, as little as 1 CFU of Salmonella in 1 ml of medium can be detected in <30 seconds. Furthermore the assay is sensitive and specific: it can detect oriC from Salmonella serovars Typhi, Paratyphi A, Paratyphi B, Paratyphi C, Typhimurium, Enteritidis and Choleraesuis but does not detect Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae or Acinetobacter baumanii. We have also performed preliminary experiments using a synthetic Salmonella oriC oligonucleotide suspended in whole human blood and observed rapid detection when the sample was diluted 1:1 with PBS. These pre-clinical data encourage progress to the next step to detect Salmonella in blood (and other ordinarily sterile, clinically relevant body fluids).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
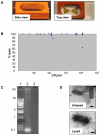


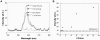
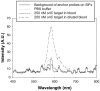
References
-
- Levine MM. Typhoid Fever Vaccines. In: Plotkin SA, Orenstein WA, editors. Vaccines. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2004. pp. 1057–1093.
-
- Voetsch AC, Van Gilder TJ, Angulo FJ, Farley MM, Shallow S, et al. FoodNet estimate of the burden of illness caused by nontyphoidal Salmonella infections in the United States. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38(Suppl 3):S127–S134. - PubMed
-
- Vugia DJ, Samuel M, Farley MM, Marcus R, Shiferaw B, et al. Invasive Salmonella infections in the United States, FoodNet, 1996–1999: incidence, serotype distribution, and outcome. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38(Suppl 3):S149–S156. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy M, Villar R, Vugia DJ, Rabatsky-Ehr T, Farley MM, et al. Hospitalizations and deaths due to Salmonella infections, FoodNet, 1996–1999. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38(Suppl 3):S142–S148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

