Dopaminergic neuronal loss, reduced neurite complexity and autophagic abnormalities in transgenic mice expressing G2019S mutant LRRK2
- PMID: 21494637
- PMCID: PMC3071839
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018568
Dopaminergic neuronal loss, reduced neurite complexity and autophagic abnormalities in transgenic mice expressing G2019S mutant LRRK2
Abstract
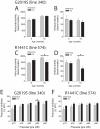
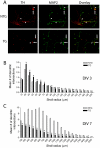
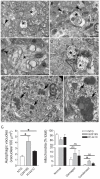
Mutations in the leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) gene cause late-onset, autosomal dominant familial Parkinson's disease (PD) and also contribute to idiopathic PD. LRRK2 mutations represent the most common cause of PD with clinical and neurochemical features that are largely indistinguishable from idiopathic disease. Currently, transgenic mice expressing wild-type or disease-causing mutants of LRRK2 have failed to produce overt neurodegeneration, although abnormalities in nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurotransmission have been observed. Here, we describe the development and characterization of transgenic mice expressing human LRRK2 bearing the familial PD mutations, R1441C and G2019S. Our study demonstrates that expression of G2019S mutant LRRK2 induces the degeneration of nigrostriatal pathway dopaminergic neurons in an age-dependent manner. In addition, we observe autophagic and mitochondrial abnormalities in the brains of aged G2019S LRRK2 mice and markedly reduced neurite complexity of cultured dopaminergic neurons. These new LRRK2 transgenic mice will provide important tools for understanding the mechanism(s) through which familial mutations precipitate neuronal degeneration and PD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Gasser T. Mendelian forms of Parkinson's disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009;1792:587–596. - PubMed
-
- Paisan-Ruiz C, Jain S, Evans EW, Gilks WP, Simon J, et al. Cloning of the gene containing mutations that cause PARK8-linked Parkinson's disease. Neuron. 2004;44:595–600. - PubMed
-
- Zimprich A, Biskup S, Leitner P, Lichtner P, Farrer M, et al. Mutations in LRRK2 cause autosomal-dominant parkinsonism with pleomorphic pathology. Neuron. 2004;44:601–607. - PubMed
-
- Moore DJ. The biology and pathobiology of LRRK2: implications for Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2008;14:S92–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

