Locating the reference point of symphysis pubis in axial CT images
- PMID: 21494903
- PMCID: PMC3264719
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-011-9384-z
Locating the reference point of symphysis pubis in axial CT images
Abstract
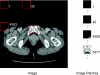
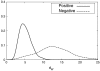
In this paper, we present an effective method to determine the reference point of symphysis pubis (SP) in an axial stack of CT images to facilitate image registration for pelvic cancer treatment. In order to reduce the computational time, the proposed method consists of two detection parts, the coarse detector, and the fine detector. The detectors check each image patch whether it contains the characteristic structure of SP. The coarse detector roughly determines the location of the reference point of SP using three types of information, which are the location and intensity of an image patch, the SP appearance, and the geometrical structure of SP. The fine detector examines around the location found by the coarse detection to refine the location of the reference point of SP. In the experiment, the average location error of the propose method was 2.23 mm, which was about the side length of two pixels. Considering that the average location error by a radiologist is 0.77 mm, the proposed method finds the reference point quite accurately. Since it takes about 10 s to locate the reference point from a stack of CT images, it is fast enough to use in real time to facilitate image registration of CT images for pelvic cancer treatment.
Figures








References
-
- Hayat M. Cancer Imaging Volume 2: Instrumentation and applications. New York: Academic; 2007.
-
- Hajnal JV, Hawkes DJ, Hill DL. Medical image registration. New York: CRC; 2001.
-
- Zitova B, Flusser J. Image registration methods: a survey. Image Vis Comput. 2003;21(11):977–1000. doi: 10.1016/S0262-8856(03)00137-9. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

