Cognitive status correlates with white matter alteration in Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 21495116
- PMCID: PMC6870034
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.21245
Cognitive status correlates with white matter alteration in Parkinson's disease
Abstract
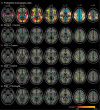
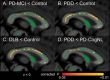
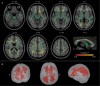
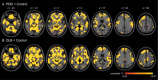
Patients with Parkinson's disease (PD) can develop mild cognitive impairment (PD-MCI), frequently progressing to dementia (PDD). Here, we aimed to elucidate the relationship between white matter alteration and cognitive status in PD and dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) by using diffusion tensor imaging. We also compared the progression patterns of white and gray matter and the cerebral perfusion. We enrolled patients with PD cognitively normal (PD-CogNL, n = 32), PD-MCI (n = 28), PDD (n = 25), DLB (n = 29), and age- and sex-matched healthy control subjects (n = 40). Fractional anisotropy (FA) map of a patient group was compared with that of control subjects by using tract-based spatial statistics. For the patient cohort, intersubject voxel-wise correlation was performed between FA values and Mini-Mental Status Examination (MMSE) scores. We also evaluated the gray matter and the cerebral perfusion by conducting a voxel-based analysis. There were significantly decreased FA values in many major tracts in patients with PD-MCI, PDD, and DLB, but not in PD-CogNL, compared with control subjects. FA values in the certain white matter areas, particularly the bilateral parietal white matter, were significantly correlated with MMSE scores in patients with PD. Patients with PDD and DLB had diffuse gray matter atrophy. All patient groups had occipital and posterior parietal hypoperfusion when compared with control subjects. Our results suggest that white matter damage underlies cognitive impairment in PD, and cognitive impairment in PD progresses with functional alteration (hypoperfusion) followed by structural alterations in which white matter alteration precedes gray matter atrophy.
Copyright © 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Relationship between cognitive impairment and white-matter alteration in Parkinson's disease with dementia: tract-based spatial statistics and tract-specific analysis.Eur Radiol. 2013 Jul;23(7):1946-55. doi: 10.1007/s00330-013-2775-4. Epub 2013 Feb 13. Eur Radiol. 2013. PMID: 23404139 Free PMC article.
-
Gray and white matter imaging: A biomarker for cognitive impairment in early Parkinson's disease?Mov Disord. 2016 Jan;31(1):103-10. doi: 10.1002/mds.26312. Epub 2015 Jul 22. Mov Disord. 2016. PMID: 26202802
-
A comparative analysis of cognitive profiles and white-matter alterations using voxel-based diffusion tensor imaging between patients with Parkinson's disease dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2010 Mar;81(3):320-6. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2009.184747. Epub 2009 Oct 14. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 19828477
-
Diffusion tensor imaging in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment.Behav Neurol. 2009;21(1):39-49. doi: 10.3233/BEN-2009-0234. Behav Neurol. 2009. PMID: 19847044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radionuclide brain imaging correlates of cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease (PD).J Neurol Sci. 2011 Nov 15;310(1-2):31-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2011.06.053. Epub 2011 Jul 16. J Neurol Sci. 2011. PMID: 21762928 Review.
Cited by
-
Entorhinal Cortex Atrophy in Early, Drug-naive Parkinson's Disease with Mild Cognitive Impairment.Aging Dis. 2019 Dec 1;10(6):1221-1232. doi: 10.14336/AD.2018.1116. eCollection 2019 Dec. Aging Dis. 2019. PMID: 31788334 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Functional Interactions of Inhibition Regions in Cognitively Normal Parkinson's Disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2018 Oct 23;10:331. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00331. eCollection 2018. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30405399 Free PMC article.
-
Functional brain networks and cognitive deficits in Parkinson's disease.Hum Brain Mapp. 2014 Sep;35(9):4620-34. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22499. Epub 2014 Mar 17. Hum Brain Mapp. 2014. PMID: 24639411 Free PMC article.
-
Grey matter hypometabolism and atrophy in Parkinson's disease with cognitive impairment: a two-step process.Brain. 2014 Aug;137(Pt 8):2356-67. doi: 10.1093/brain/awu159. Epub 2014 Jun 20. Brain. 2014. PMID: 24951642 Free PMC article.
-
Systems-based analyses of brain regions functionally impacted in Parkinson's disease reveals underlying causal mechanisms.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 29;9(8):e102909. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102909. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25170892 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ballard C, Ziabreva I, Perry R, Larsen JP, O'Brien J, McKeith I, Perry E, Aarsland D ( 2006): Differences in neuropathologic characteristics across the Lewy body dementia spectrum. Neurology 67: 1931–1934. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu C ( 2002): The basis of anisotropic water diffusion in the nervous system—A technical review. NMR Biomed 15: 435–455. - PubMed
-
- Beyer MK, Aarsland D, Greve OJ, Larsen JP ( 2006): Visual rating of white matter hyperintensities in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 21: 223–229. - PubMed
-
- Beyer MK, Larsen JP, Aarsland D ( 2007b): Gray matter atrophy in Parkinson disease with dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurology 69: 747–754. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

