Effect of hyoscine-N-butyl bromide rectal suppository on labor progress in primigravid women: randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 21495198
- PMCID: PMC3081214
- DOI: 10.3325/cmj.2011.52.159
Effect of hyoscine-N-butyl bromide rectal suppository on labor progress in primigravid women: randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Aim: To determine the effects of hyoscine-N-butyl bromide (HBB) rectal suppository on labor progress in primigravid women.
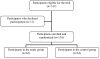
Methods: A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial was carried out on 130 primigravid women admitted for spontaneous labor. The women were recruited based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria and randomized into the experimental (n=65) and control group (n=65). In the beginning of the active phase of labor, 20 mg of HBB rectal suppository was administered to the experimental group, while a placebo suppository was administered to the control group. Cervical dilatation and duration of active phase and second stage of labor were recorded.
Results: The rate of cervical dilatation was 2.6 cm/h in the experimental and 1.5 cm/h in the control group (P<0.001). The active phase and the second stage of labor were significantly shorter in the experimental group (P=0.001 and P<0.001, respectively). There was no significant difference between the two groups in the fetal heart rate, maternal pulse rate, blood pressure, and the APGAR score 1 and 5 minutes after birth.
Conclusion: Use of HBB rectal suppository in the active management of labor can shorten both the active phase and second stage of labor without significant side-effects.
Figures
References
-
- O'Driscoll K, Foley M. Correlation of decrease in perinatal mortality and increase in cesarean section rates. Obstet Gynecol. 1983;61:1–5. - PubMed
-
- O'Driscoll K, Foley M, MacDonald D. Active management of labor as an alternative to cesarean section for dystocia. Obstet Gynecol. 1984;63:485–90. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources