Clinical management of aplastic anemia
- PMID: 21495931
- PMCID: PMC3138728
- DOI: 10.1586/ehm.11.11
Clinical management of aplastic anemia
Abstract
Acquired aplastic anemia is a potentially fatal bone marrow failure disorder that is characterized by pancytopenia and a hypocellular bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation or bone marrow transplantation (BMT) is the treatment of choice for young patients who have a matched sibling donor. Immunosuppression with either anti-thymocyte globulin and cyclosporine or high-dose cyclophosphamide is an effective therapy for patients who are not suitable BMT candidates owing to age or lack of a suitable donor. Results of BMT from unrelated and mismatched donors are improving, but presently this treatment option is best reserved for those patients who do not respond, relapse or develop secondary clonal disorders following immunosuppressive therapy. Efforts are currently underway to both improve immunosuppressive regimens and to expand the application of BMT.
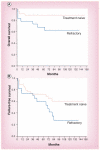
Figures
References
-
- Ehrlich P. [On the case of anemia with remarks on regenerative bone marrow changes] Charite-Annalen. 1888;13:301–309.
-
- Nakanishi K, Taniguchi T, Ranganathan V, et al. Interaction of FANCD2 and NBS1 in the DNA damage response. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002;4(12):913–920. - PubMed
-
- Uechi T, Nakajima Y, Chakraborty A, Torihara H, Higa S, Kenmochi N. Deficiency of ribosomal protein S19 during early embryogenesis leads to reduction of erythrocytes in a zebrafish model of Diamond–Blackfan anemia. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008;17(20):3204–3211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
