MIR29B regulates expression of MLLT11 (AF1Q), an MLL fusion partner, and low MIR29B expression associates with adverse cytogenetics and poor overall survival in AML
- PMID: 21496004
- PMCID: PMC3896048
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.2011.08662.x
MIR29B regulates expression of MLLT11 (AF1Q), an MLL fusion partner, and low MIR29B expression associates with adverse cytogenetics and poor overall survival in AML
Abstract
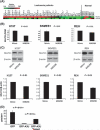
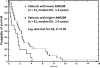
MLLT11, an MLL fusion partner, is a poor prognostic biomarker for paediatric acute myeloid leukaemia (AML), adult normal cytogenetics AML, and adult myelodysplastic syndrome. MLLT11 is highly regulated during haematopoietic progenitor differentiation and development but its regulatory mechanisms have not been defined. In this study, we demonstrate by transfection experiments that MIR29B directly regulates MLLT11 expression in vitro. MIR29B expression level was also inversely related to MLLT11 expression in a cohort of 56 AML patients (P<0·05). AML patients with low MIR29B/elevated MLLT11 expression had poor overall survival (P=0·038). Therefore, MIR29B may be a potential prognostic biomarker for AML patients.
© 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Ambros V. microRNAs: tiny regulators with great potential. Cell. 2001;107:823–826. - PubMed
-
- Garzon R, Garofalo M, Martelli MP, Briesewitz R, Wang L, Fernandez-Cymering C, Volinia S, Liu CG, Schnittger S, Haferlach T, Liso A, Diverio D, Mancini M, Meloni G, Foa R, Martelli MF, Mecucci C, Croce CM, Falini B. Distinctive microRNA signature of acute myeloid leukemia bearing cytoplasmic mutated nucleophosmin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2008;105:3945–3950. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Garzon R, Liu S, Fabbri M, Liu Z, Heaphy CE, Callegari E, Schwind S, Pang J, Yu J, Muthusamy N, Havelange V, Volinia S, Blum W, Rush LJ, Perrotti D, Andreeff M, Bloomfield CD, Byrd JC, Chan K, Wu LC, Croce CM, Marcucci G. MicroRNA-29b induces global DNA hypomethylation and tumor suppressor gene reexpression in acute myeloid leukemia by targeting directly DNMT3A and 3B and indirectly DNMT1. Blood. 2009;113:6411–6418. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li Z, Lu J, Sun M, Mi S, Zhang H, Luo RT, Chen P, Wang Y, Yan M, Qian Z, Neilly MB, Jin J, Zhang Y, Bohlander SK, Zhang DE, Larson RA, Le Beau MM, Thirman MJ, Golub TR, Rowley JD, Chen J. Distinct microRNA expressionprofiling in acute myeloid leukemia with common translocation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2008;105:15535–15540. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

