FungalRV: adhesin prediction and immunoinformatics portal for human fungal pathogens
- PMID: 21496229
- PMCID: PMC3224177
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-192
FungalRV: adhesin prediction and immunoinformatics portal for human fungal pathogens
Abstract
Background: The availability of sequence data of human pathogenic fungi generates opportunities to develop Bioinformatics tools and resources for vaccine development towards benefitting at-risk patients.
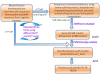
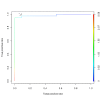
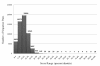
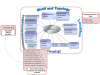
Description: We have developed a fungal adhesin predictor and an immunoinformatics database with predicted adhesins. Based on literature search and domain analysis, we prepared a positive dataset comprising adhesin protein sequences from human fungal pathogens Candida albicans, Candida glabrata, Aspergillus fumigatus, Coccidioides immitis, Coccidioides posadasii, Histoplasma capsulatum, Blastomyces dermatitidis, Pneumocystis carinii, Pneumocystis jirovecii and Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. The negative dataset consisted of proteins with high probability to function intracellularly. We have used 3945 compositional properties including frequencies of mono, doublet, triplet, and multiplets of amino acids and hydrophobic properties as input features of protein sequences to Support Vector Machine. Best classifiers were identified through an exhaustive search of 588 parameters and meeting the criteria of best Mathews Correlation Coefficient and lowest coefficient of variation among the 3 fold cross validation datasets. The "FungalRV adhesin predictor" was built on three models whose average Mathews Correlation Coefficient was in the range 0.89-0.90 and its coefficient of variation across three fold cross validation datasets in the range 1.2% - 2.74% at threshold score of 0. We obtained an overall MCC value of 0.8702 considering all 8 pathogens, namely, C. albicans, C. glabrata, A. fumigatus, B. dermatitidis, C. immitis, C. posadasii, H. capsulatum and P. brasiliensis thus showing high sensitivity and specificity at a threshold of 0.511. In case of P. brasiliensis the algorithm achieved a sensitivity of 66.67%. A total of 307 fungal adhesins and adhesin like proteins were predicted from the entire proteomes of eight human pathogenic fungal species. The immunoinformatics analysis data on these proteins were organized for easy user interface analysis. A Web interface was developed for analysis by users. The predicted adhesin sequences were processed through 18 immunoinformatics algorithms and these data have been organized into MySQL backend. A user friendly interface has been developed for experimental researchers for retrieving information from the database.
Conclusion: FungalRV webserver facilitating the discovery process for novel human pathogenic fungal adhesin vaccine has been developed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
FaaPred: a SVM-based prediction method for fungal adhesins and adhesin-like proteins.PLoS One. 2010 Mar 15;5(3):e9695. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009695. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20300572 Free PMC article.
-
MAAP: malarial adhesins and adhesin-like proteins predictor.Proteins. 2008 Feb 15;70(3):659-66. doi: 10.1002/prot.21568. Proteins. 2008. PMID: 17879344
-
Immunoinformatics as a Tool for New Antifungal Vaccines.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1625:31-43. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7104-6_3. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28584981
-
Highlights in pathogenic fungal biofilms.Rev Iberoam Micol. 2014 Jan-Mar;31(1):22-9. doi: 10.1016/j.riam.2013.09.014. Epub 2013 Nov 16. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2014. PMID: 24252828 Review.
-
Preventative and therapeutic vaccines for fungal infections: from concept to implementation.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2004 Dec;3(6):701-9. doi: 10.1586/14760584.3.6.701. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2004. PMID: 15606355 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative genomics of the major fungal agents of human and animal Sporotrichosis: Sporothrix schenckii and Sporothrix brasiliensis.BMC Genomics. 2014 Oct 29;15:943. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-943. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 25351875 Free PMC article.
-
Host-specific targets of Histomonas meleagridis antigens revealed by immunoprecipitation.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 17;15(1):5800. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88855-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39962091 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of vaccine targets & design of vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus using computational and deep learning-based approaches.PeerJ. 2022 May 19;10:e13380. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13380. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35611169 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of vaccine targets in pathogens and design of a vaccine using computational approaches.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 2;11(1):17626. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-96863-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34475453 Free PMC article.
-
The New GPI-Anchored Protein, SwgA, Is Involved in Nitrogen Metabolism in the Pathogenic Filamentous Fungus Aspergillus fumigatus.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Feb 15;9(2):256. doi: 10.3390/jof9020256. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836370 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vazquez JA, Sobel JD. In: Clinical Mycology. Dismukes WE, Pappas PG, Sobel JD, editor. Oxford Univers; 2003. Candidiasis; pp. 143–187.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

