Prospective evaluation of prognostic factors uPA/PAI-1 in node-negative breast cancer: phase III NNBC3-Europe trial (AGO, GBG, EORTC-PBG) comparing 6×FEC versus 3×FEC/3×Docetaxel
- PMID: 21496284
- PMCID: PMC3089797
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-140
Prospective evaluation of prognostic factors uPA/PAI-1 in node-negative breast cancer: phase III NNBC3-Europe trial (AGO, GBG, EORTC-PBG) comparing 6×FEC versus 3×FEC/3×Docetaxel
Abstract
Background: Today, more than 70% of patients with primary node-negative breast cancer are cured by local therapy alone. Many patients receive overtreatment by adjuvant chemotherapy due to inadequate risk assessment. So far, few clinical trials have prospectively evaluated tumor biology based prognostic factors. Risk assessment by a biological algorithm including invasion factors urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and its inhibitor plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 (PAI-1) will assess up to 35-55% of node-negative patients as low-risk and thus avoid chemotherapy. In contrast, a clinical-pathological algorithm will only classify 20-40% of patients as low-risk. High-risk node-negative patients should receive chemotherapy. Anthracycline-based regimens are accepted as a standard, the additional benefit of taxanes remains an open question.
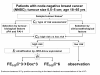
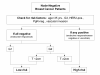
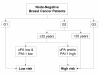
Methods/design: The international NNBC3 ("Node Negative Breast Cancer 3-Europe") trial compares biological risk assessment (UP) using invasion factors uPA/PAI-1 with a clinical-pathological algorithm (CP). In this trial, the type of risk assessment (CP or UP) was chosen upfront by each center for its patients. Fresh frozen tissue was obtained to determine uPA/PAI-1 using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Patients assessed as high-risk were stratified by human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) status and then randomised to receive anthracycline-containing chemotherapy 5-Fluorouracil (F)/Epirubicin (E)/Cyclophosphymide (C) or an anthracycline-taxane sequence (FE(100)C*6 versus FE(100)C*3 followed by Docetaxel(100)*3).
Discussion: In this trial, 4,149 node-negative patients with operable breast cancer from 153 centers in Germany and France were included since 2002. Measurement of uPA/PAI-1 by ELISA was performed with standardised central quality assurance for 2,497 patients (60%) from 56 "UP"-centers. The NNBC 3-Europe trial showed that inclusion of patients into a clinical phase III trial is feasible based on biological testing of fresh frozen tumor material. In addition, 2,661 patients were classified as high-risk and thus received chemotherapy. As adjuvant chemotherapy, 1,334 high-risk patients received FE(100)C-Docetaxel(100), and 1,327 received French FE(100)C. No unexpected toxicities were observed. Chemotherapy efficacy and comparison of UP with CP will be evaluated after longer follow-up.
Trial registration: clinical Trials.gov NCT01222052.
© 2011 Kantelhardt et al; licensee BioMed Central Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Harbeck N, Alt U, Berger U, Krüger A, Thomssen C, Jänicke F, Höfler H, Kates RE, Schmitt M. Prognostic impact of proteolytic factors (urokinase-type plasminogen activator, plasminogen activator inhibitor 1, and cathepsins B, D, and L) in primary breast cancer reflects effects of adjuvant systemic therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:2757–64. - PubMed
-
- Jänicke F, Prechtl A, Thomssen C, Harbeck N, Meisner C, Untch M, Sweep CG, Selbmann HK, Graeff H, Schmitt M. German N0 Study Group. Randomized adjuvant chemotherapy trial in high-risk, lymph node-negative breast cancer patients identified by urokinase-type plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93:913–20. - PubMed
-
- Cufer T, Borstnar S, Vrhovec I. Prognostic and predictive value of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) and its inhibitors PAI-1 and PAI-2 in operable breast cancer. Int J Biol Markers. 2003;18:106–115. - PubMed
-
- Jänicke F, Schmitt M, Pache L, Ulm K, Harbeck N, Höfler H, Graeff H. Urokinase (uPA) and its inhibitor PAI-1 are strong and independent prognostic factors in node-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1993;24:195–208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

