Hands-free, wireless goggles for near-infrared fluorescence and real-time image-guided surgery
- PMID: 21496565
- PMCID: PMC3079879
- DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2011.02.007
Hands-free, wireless goggles for near-infrared fluorescence and real-time image-guided surgery
Abstract
Background: Current cancer management faces several challenges, including the occurrence of a residual tumor after resection, the use of radioactive materials or high concentrations of blue dyes for sentinel lymph node biopsy, and the use of bulky systems in surgical suites for image guidance. To overcome these limitations, we developed a real-time, intraoperative imaging device that, when combined with near infrared fluorescent molecular probes, can aid in the identification of tumor margins, guide surgical resections, map sentinel lymph nodes, and transfer acquired data wirelessly for remote analysis.
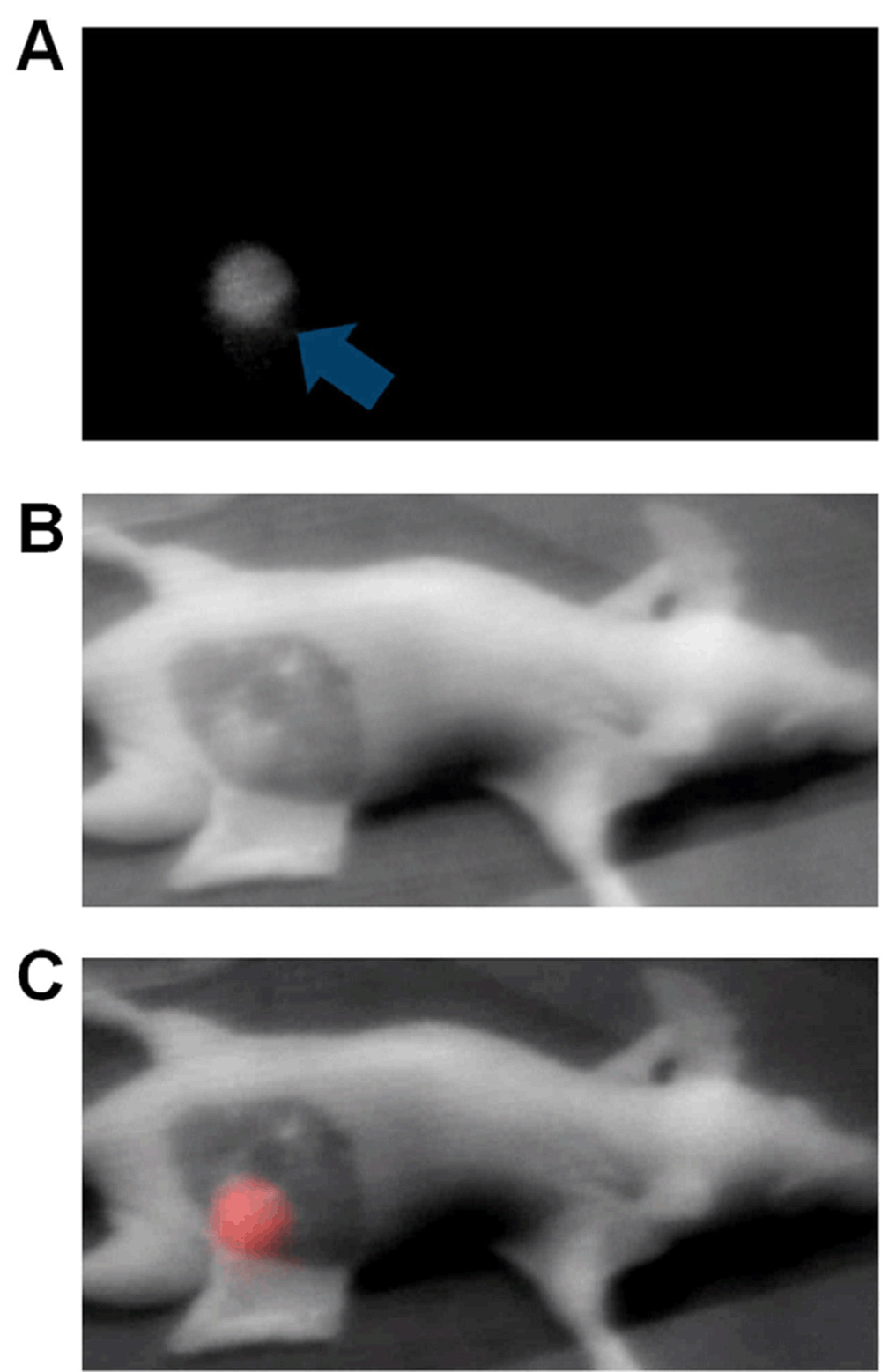
Methods: We developed a new compact, wireless, wearable, and battery-operated device that allows for hands-free operation by surgeons. A charge-coupled device-based, consumer-grade night vision viewer was used to develop the detector portion of the device, and the light source portion was developed from a compact headlamp. This piece was retrofitted to provide both near infrared excitation and white light illumination simultaneously. Wireless communication was enabled by integrating a battery-operated, miniature, radio-frequency video transmitter into the system. We applied the device in several types of oncologic surgical procedures in murine models, including sentinel lymph node mapping, fluorescence-guided tumor resection, and surgery under remote expert guidance.
Results: Unlike conventional imaging instruments, the device displays fluorescence information directly on its eyepiece. When employed in sentinel lymph node mapping, the locations of sentinel lymph nodes were visualized clearly, even with tracer level dosing of a near infrared fluorescent dye (indocyanine green). When used in tumor resection, tumor margins and small nodules invisible to the naked eye were visualized readily. In a simulated, point-of-care setting, tumors were located successfully and removed under remote guidance using the wireless feature of the device. Importantly, the total cost of this prototype system ($1200) is substantially less than existing imaging instruments.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate the feasibility of using the new device to aid surgical resection of tumors, map sentinel lymph nodes, and facilitate telemedicine.
Copyright © 2011 Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Collins L, et al. Outcome of Women with Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS) Treated with Breast-Conserving Surgery Alone: A Case-Control Study of 225 Patients from the Cancer Research Network. Modern Pathology. 2009;22:34A–35A.
-
- Vicini FA, et al. Impact of young age on outcome in patients with ductal carcinoma-in-situ treated with breast-conserving therapy. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2000;18:296–306. - PubMed
-
- Albo D, et al. Anaphylactic reactions to isosulfan blue dye during sentinel lymph node biopsy for breast cancer. American Journal of Surgery. 2001;182:393–398. - PubMed
-
- Amr D, Broderick-Villa G, Haigh PI, Guenther JM, DiFronzo LA. Adverse drug reactions during lymphatic mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy for solid neoplasms. American Surgeon. 2005;71:720–724. - PubMed
-
- Aydogan F, Celik V, Uras C, Salihoglu Z, Topuz U. A comparison of the adverse reactions associated with isosulfan blue versus methylene blue dye in sentinel lymph node biopsy for breast cancer. American Journal of Surgery. 2008;195:277–278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

