Thermal robustness of signaling in bacterial chemotaxis
- PMID: 21496648
- PMCID: PMC3098529
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.03.013
Thermal robustness of signaling in bacterial chemotaxis
Abstract
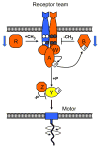
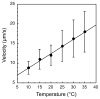
Temperature is a global factor that affects the performance of all intracellular networks. Robustness against temperature variations is thus expected to be an essential network property, particularly in organisms without inherent temperature control. Here, we combine experimental analyses with computational modeling to investigate thermal robustness of signaling in chemotaxis of Escherichia coli, a relatively simple and well-established model for systems biology. We show that steady-state and kinetic pathway parameters that are essential for chemotactic performance are indeed temperature-compensated in the entire physiological range. Thermal robustness of steady-state pathway output is ensured at several levels by mutual compensation of temperature effects on activities of individual pathway components. Moreover, the effect of temperature on adaptation kinetics is counterbalanced by preprogrammed temperature dependence of enzyme synthesis and stability to achieve nearly optimal performance at the growth temperature. Similar compensatory mechanisms are expected to ensure thermal robustness in other systems.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Design principles of a bacterial signalling network.Nature. 2005 Nov 24;438(7067):504-7. doi: 10.1038/nature04228. Nature. 2005. PMID: 16306993
-
Single-cell FRET imaging of phosphatase activity in the Escherichia coli chemotaxis system.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Dec 7;101(49):17072-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407812101. Epub 2004 Nov 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15569922 Free PMC article.
-
Precision and kinetics of adaptation in bacterial chemotaxis.Biophys J. 2010 Nov 3;99(9):2766-74. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.08.051. Biophys J. 2010. PMID: 21044573 Free PMC article.
-
Chemotaxis: how bacteria use memory.Biol Chem. 2009 Nov;390(11):1097-104. doi: 10.1515/BC.2009.130. Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19747082 Review.
-
Information processing in bacteria: memory, computation, and statistical physics: a key issues review.Rep Prog Phys. 2016 May;79(5):052601. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/79/5/052601. Epub 2016 Apr 8. Rep Prog Phys. 2016. PMID: 27058315 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phenotypic diversity and temporal variability in a bacterial signaling network revealed by single-cell FRET.Elife. 2017 Dec 12;6:e27455. doi: 10.7554/eLife.27455. Elife. 2017. PMID: 29231170 Free PMC article.
-
Fundamental constraints on the abundances of chemotaxis proteins.Biophys J. 2015 Mar 10;108(5):1293-305. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2015.01.024. Biophys J. 2015. PMID: 25762341 Free PMC article.
-
Behaviors and strategies of bacterial navigation in chemical and nonchemical gradients.PLoS Comput Biol. 2014 Jun 19;10(6):e1003672. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003672. eCollection 2014 Jun. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014. PMID: 24945282 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial chemoreceptors and chemoeffectors.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Feb;72(4):691-708. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1770-5. Epub 2014 Nov 6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25374297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Network crosstalk dynamically changes during neutrophil polarization.Cell. 2012 May 25;149(5):1073-83. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.044. Cell. 2012. PMID: 22632971 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alon U, Surette MG, Barkai N, Leibler S. Robustness in bacterial chemotaxis. Nature. 1999;397:168–171. - PubMed
-
- Barkai N, Leibler S. Robustness in simple biochemical networks. Nature. 1997;387:913–917. - PubMed
-
- Berg HC, Brown DA. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli analysed by three-dimensional tracking. Nature. 1972;239:500–504. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

