Hydroxylation of 5-methylcytosine by TET1 promotes active DNA demethylation in the adult brain
- PMID: 21496894
- PMCID: PMC3088758
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.03.022
Hydroxylation of 5-methylcytosine by TET1 promotes active DNA demethylation in the adult brain
Abstract
Cytosine methylation is the major covalent modification of mammalian genomic DNA and plays important roles in transcriptional regulation. The molecular mechanism underlying the enzymatic removal of this epigenetic mark, however, remains elusive. Here, we show that 5-methylcytosine (5mC) hydroxylase TET1, by converting 5mCs to 5-hydroxymethylcytosines (5hmCs), promotes DNA demethylation in mammalian cells through a process that requires the base excision repair pathway. Though expression of the 12 known human DNA glycosylases individually did not enhance removal of 5hmCs in mammalian cells, demethylation of both exogenously introduced and endogenous 5hmCs is promoted by the AID (activation-induced deaminase)/APOBEC (apolipoprotein B mRNA-editing enzyme complex) family of cytidine deaminases. Furthermore, Tet1 and Apobec1 are involved in neuronal activity-induced, region-specific, active DNA demethylation and subsequent gene expression in the dentate gyrus of the adult mouse brain in vivo. Our study suggests a TET1-induced oxidation-deamination mechanism for active DNA demethylation in mammals.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
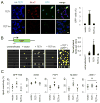
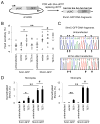
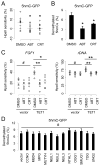
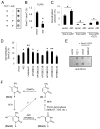
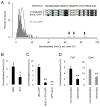
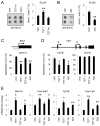
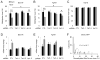
References
-
- Baker D, Liu P, Burdzy A, Sowers LC. Characterization of the substrate specificity of a human 5-hydroxymethyluracil glycosylase activity. Chem Res Toxicol. 2002;15:33–39. - PubMed
-
- Boorstein RJ, Cummings A, Jr, Marenstein DR, Chan MK, Ma Y, Neubert TA, Brown SM, Teebor GW. Definitive identification of mammalian 5-hydroxymethyluracil DNA N-glycosylase activity as SMUG1. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:41991–41997. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HD069184/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH087874/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG024984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS048271/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS047344/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- MH087874/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R56 NS047344/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS048271/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS047344/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AG024984/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R33 MH087874/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HD069184/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- NS047344/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

