Topological constraints: using RNA secondary structure to model 3D conformation, folding pathways, and dynamic adaptation
- PMID: 21497083
- PMCID: PMC3319143
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sbi.2011.03.009
Topological constraints: using RNA secondary structure to model 3D conformation, folding pathways, and dynamic adaptation
Abstract
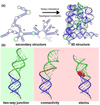
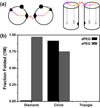
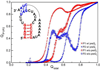
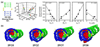
Accompanying recent advances in determining RNA secondary structure is the growing appreciation for the importance of relatively simple topological constraints, encoded at the secondary structure level, in defining the overall architecture, folding pathways, and dynamic adaptability of RNA. A new view is emerging in which tertiary interactions do not define RNA 3D structure, but rather, help select specific conformers from an already narrow, topologically pre-defined conformational distribution. Studies are providing fundamental insights into the nature of these topological constraints, how they are encoded by the RNA secondary structure, and how they interplay with other interactions, breathing new meaning to RNA secondary structure. New approaches have been developed that take advantage of topological constraints in determining RNA backbone conformation based on secondary structure, and a limited set of other, easily accessible constraints. Topological constraints are also providing a much-needed framework for rationalizing and describing RNA dynamics and structural adaptation. Finally, studies suggest that topological constraints may play important roles in steering RNA folding pathways. Here, we review recent advances in our understanding of topological constraints encoded by the RNA secondary structure.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
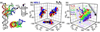
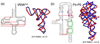
References
-
- Murthy VL, Srinivasan R, Draper DE, Rose GD. A complete conformational map for RNA. J Mol Biol. 1999;291:313–327. - PubMed
-
- Musselman C, Pitt SW, Gulati K, Foster LL, Andricioaei I, Al-Hashimi HM. Impact of static and dynamic A-form heterogeneity on the determination of RNA global structural dynamics using NMR residual dipolar couplings. J Biomol NMR. 2006;36:235–249. - PubMed
-
- Riordan FA, Bhattacharyya A, McAteer S, Lilley DM. Kinking of RNA helices by bulged bases, and the structure of the human immunodeficiency virus transactivator response element. J Mol Biol. 1992;226:305–310. - PubMed
-
- Lilley DM. Structures of helical junctions in nucleic acids. Q Rev Biophys. 2000;33:109–159. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

