More than a splicing code: integrating the role of RNA, chromatin and non-coding RNA in alternative splicing regulation
- PMID: 21497503
- PMCID: PMC6317717
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gde.2011.03.004
More than a splicing code: integrating the role of RNA, chromatin and non-coding RNA in alternative splicing regulation
Abstract
Large portions of the genome undergo alternative pre-mRNA splicing in often intricate patterns. Alternative splicing regulation requires extensive control mechanisms since errors can have deleterious consequences and may lead to developmental defects and disease. Recent work has identified a complex network of regulatory RNA elements which guide splicing decisions. In addition, the discovery that transcription and splicing are intimately coupled has opened up new directions into alternative splicing regulation. Work at the interface of chromatin and RNA biology has revealed unexpected molecular links between histone modifications, the transcription machinery, and non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) in the determination of alternative splicing patterns.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
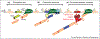

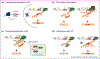
References
-
-
Wang ET, Sandberg R, Luo S, Khrebtukova I, Zhang L, Mayr C, Kingsmore SF, Schroth GP, Burge CB: Alternative isoform regulation in human tissue transcriptomes. Nature 2008.
One of the first genome-wide studies based on RNA deep-sequencing which revealed that large portions of the human genome are alternatively spliced in a highly tissue-specific fashion.
-
-
- Wang GS, Cooper TA: Splicing in disease: disruption of the splicing code and the decoding machinery. Nat Rev Genet 2007, 8:749–761. - PubMed
-
- Venables JP: Aberrant and alternative splicing in cancer. Cancer Res 2004, 64:7647–7654. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

