Quantitation of dissolved gas content in emulsions and in blood using mass spectrometric detection
- PMID: 21497566
- PMCID: PMC3107015
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2011.03.041
Quantitation of dissolved gas content in emulsions and in blood using mass spectrometric detection
Abstract
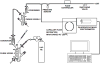
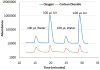
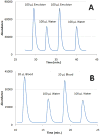
Quantitation of dissolved gases in blood or in other biological media is essential for understanding the dynamics of metabolic processes. Current detection techniques, while enabling rapid and convenient assessment of dissolved gases, provide only direct information on the partial pressure of gases dissolved in the aqueous fraction of the fluid. The more relevant quantity known as gas content, which refers to the total amount of the gas in all fractions of the sample, can be inferred from those partial pressures, but only indirectly through mathematical modeling. Here we describe a simple mass spectrometric technique for rapid and direct quantitation of gas content for a wide range of gases. The technique is based on a mass spectrometer detector that continuously monitors gases that are rapidly extracted from samples injected into a purge vessel. The accuracy and sample processing speed of the system is demonstrated with experiments that reproduce within minutes literature values for the solubility of various gases in water. The capability of the technique is further demonstrated through accurate determination of O(2) content in a lipid emulsion and in whole blood, using as little as 20 μL of sample. The approach to gas content quantitation described here should greatly expand the range of animals and conditions that may be used in studies of metabolic gas exchange, and facilitate the development of artificial oxygen carriers and resuscitation fluids.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Kilburn DG, Webb FC. Biotechnology and Bioengineering. 1968;10:801. - PubMed
-
- Severinghaus JW, Astrup P, Murray JF. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1998;157:S114. - PubMed
-
- Hoch G, Kok B. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963;101:160. - PubMed
-
- Seylaz J, Pinard E, Meric P, Correze JL. Am J Physiol. 1983;245:H513. - PubMed
-
- Tu C, Swenson ER, Silverman DN. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007;43:1453. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

