Society of Thoracic Surgeons Risk Score predicts hospital charges and resource use after aortic valve replacement
- PMID: 21497834
- PMCID: PMC3156832
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2011.02.038
Society of Thoracic Surgeons Risk Score predicts hospital charges and resource use after aortic valve replacement
Abstract
Objective: The impact of Society of Thoracic Surgeons predicted mortality risk score on resource use has not been previously studied. We hypothesize that increasing Society of Thoracic Surgeons risk scores in patients undergoing aortic valve replacement are associated with greater hospital charges.
Methods: Clinical and financial data for patients undergoing aortic valve replacement at The Johns Hopkins Hospital over a 10-year period (January 2000 to December 2009) were reviewed. The current Society of Thoracic Surgeons formula (v2.61) for in-hospital mortality was used for all patients. After stratification into risk quartiles, index admission hospital charges were compared across risk strata with rank-sum and Kruskal-Wallis tests. Linear regression and Spearman's coefficient assessed correlation and goodness of fit. Multivariable analysis assessed relative contributions of individual variables on overall charges.
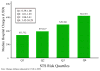
Results: A total of 553 patients underwent aortic valve replacement during the study period. Average predicted mortality was 2.9% (±3.4) and actual mortality was 3.4% for aortic valve replacement. Median charges were greater in the upper quartile of patients undergoing aortic valve replacement (quartiles 1-3, $39,949 [interquartile range, 32,708-51,323] vs quartile 4, $62,301 [interquartile range, 45,952-97,103], P < .01]. On univariate linear regression, there was a positive correlation between Society of Thoracic Surgeons risk score and log-transformed charges (coefficient, 0.06; 95% confidence interval, 0.05-0.07; P < .01). Spearman's correlation R-value was 0.51. This positive correlation persisted in risk-adjusted multivariable linear regression. Each 1% increase in Society of Thoracic Surgeons risk score was associated with an added $3000 in hospital charges.
Conclusions: This is the first study to show that increasing Society of Thoracic Surgeons risk score predicts greater charges after aortic valve replacement. As competing therapies, such as percutaneous valve replacement, emerge to treat high-risk patients, these results serve as a benchmark to compare resource use.
Copyright © 2011 The American Association for Thoracic Surgery. Published by Mosby, Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Leon MB, Smith CR, Mack M, Miller DC, Moses JW, Svensson LG, et al. Transcatheter aortic-valve implantation for aortic stenosis in patients who cannot undergo surgery. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1597–1607. - PubMed
-
- Ross J, Jr, Braunwald E. Aortic stenosis. Circulation. 1968;38:61–67. - PubMed
-
- Elbardissi AW, Shekar P, Couper GS, Cohn LH. Minimally invasive aortic valve replacement in octogenarian, high-risk, transcatheter aortic valve implantation candidates. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011;141:328–335. - PubMed
-
- Schwarz F, Baumann P, Manthey J, Hoffmann M, Schuler G, Mehmel HC, et al. The effect of aortic valve replacement on survival. Circulation. 1982;66:1105–1110. - PubMed
-
- Varadarajan P, Kapoor N, Bansal RC, Pai RG. Survival in elderly patients with severe aortic stenosis is dramatically improved by aortic valve replacement: Results from a cohort of 277 patients aged > or =80 years. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2006;30:722–727. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

