Mediator head subcomplex Med11/22 contains a common helix bundle building block with a specific function in transcription initiation complex stabilization
- PMID: 21498544
- PMCID: PMC3152362
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkr229
Mediator head subcomplex Med11/22 contains a common helix bundle building block with a specific function in transcription initiation complex stabilization
Abstract
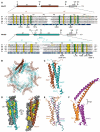
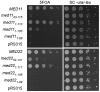
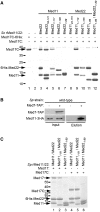
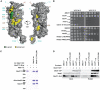
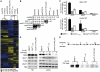
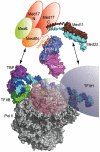
Mediator is a multiprotein co-activator of RNA polymerase (Pol) II transcription. Mediator contains a conserved core that comprises the 'head' and 'middle' modules. We present here a structure-function analysis of the essential Med11/22 heterodimer, a part of the head module. Med11/22 forms a conserved four-helix bundle domain with C-terminal extensions, which bind the central head subunit Med17. A highly conserved patch on the bundle surface is required for stable transcription pre-initiation complex formation on a Pol II promoter in vitro and in vivo and may recruit the general transcription factor TFIIH. The bundle domain fold is also present in the Mediator middle module subcomplex Med7/21 and is predicted in the Mediator heterodimers Med2/3, Med4/9, Med10/14 and Med28/30. The bundle domain thus represents a common building block that has been multiplied and functionally diversified during Mediator evolution in eukaryotes.
Figures

References
-
- Roeder RG. The role of general initiation factors in transcription by RNA polymerase II. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1996;21:327–335. - PubMed
-
- Bjorklund S, Gustafsson C. The yeast Mediator complex and its regulation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2005;30:240–244. - PubMed
-
- Kornberg R. Mediator and the mechanism of transcriptional activation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2005;30:235–239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

