H3K9 methyltransferase G9a and the related molecule GLP
- PMID: 21498567
- PMCID: PMC3078703
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.2027411
H3K9 methyltransferase G9a and the related molecule GLP
Abstract
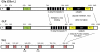
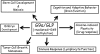
The discovery of Suv39h1, the first SET domain-containing histone lysine methyltransferase (HKMT), was reported in 2000. Since then, research on histone methylation has progressed rapidly. Among the identified HKMTs in mammals, G9a and GLP are the primary enzymes for mono- and dimethylation at Lys 9 of histone H3 (H3K9me1 and H3K9me2), and exist predominantly as a G9a-GLP heteromeric complex that appears to be a functional H3K9 methyltransferase in vivo. Recently, many important studies have reported that G9a and GLP play critical roles in various biological processes. The physiological relevance of G9a/GLP-mediated epigenetic gene regulation is discussed.
Figures
References
-
- Balemans MC, Huibers MM, Eikelenboom NW, Kuipers AJ, van Summeren RC, Pijpers MM, Tachibana M, Shinkai Y, van Bokhoven H, Van der Zee CE 2010. Reduced exploration, increased anxiety, and altered social behavior: autistic-like features of euchromatin histone methyltransferase 1 heterozygous knockout mice. Behav Brain Res 208: 47–55 - PubMed
-
- Bannister AJ, Zegerman P, Partridge JF, Miska EA, Thomas JO, Allshire RC, Kouzarides T 2001. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 410: 120–124 - PubMed
-
- Barski A, Cuddapah S, Cui K, Roh TY, Schones DE, Wang Z, Wei G, Chepelev I, Zhao K 2007. High-resolution profiling of histone methylations in the human genome. Cell 129: 823–837 - PubMed
-
- Bostick M, Kim JK, Estève PO, Clark A, Pradhan S, Jacobsen SE 2007. UHRF1 plays a role in maintaining DNA methylation in mammalian cells. Science 317: 1760–1764 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
