Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 directly regulates murine neurogenesis
- PMID: 21498572
- PMCID: PMC3078708
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.615311
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 directly regulates murine neurogenesis
Abstract
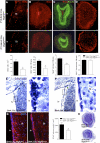
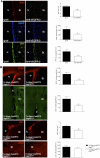
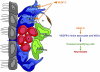
Neural stem cells (NSCs) are slowly dividing astrocytes that are intimately associated with capillary endothelial cells in the subventricular zone (SVZ) of the brain. Functionally, members of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family can stimulate neurogenesis as well as angiogenesis, but it has been unclear whether they act directly via VEGF receptors (VEGFRs) expressed by neural cells, or indirectly via the release of growth factors from angiogenic capillaries. Here, we show that VEGFR-3, a receptor required for lymphangiogenesis, is expressed by NSCs and is directly required for neurogenesis. Vegfr3:YFP reporter mice show VEGFR-3 expression in multipotent NSCs, which are capable of self-renewal and are activated by the VEGFR-3 ligand VEGF-C in vitro. Overexpression of VEGF-C stimulates VEGFR-3-expressing NSCs and neurogenesis in the SVZ without affecting angiogenesis. Conversely, conditional deletion of Vegfr3 in neural cells, inducible deletion in subventricular astrocytes, and blocking of VEGFR-3 signaling with antibodies reduce SVZ neurogenesis. Therefore, VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 signaling acts directly on NSCs and regulates adult neurogenesis, opening potential approaches for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
Figures
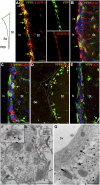
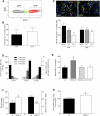
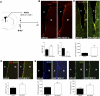
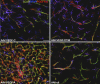
References
-
- Acker T, Beck H, Plate KH 2001. Cell type specific expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietin-1 and -2 suggests an important role of astrocytes in cerebellar vascularization. Mech Dev 108: 45–57 - PubMed
-
- Bock F, Onderka J, Dietrich T, Bachmann B, Pytowski B, Cursiefen C 2008. Blockade of VEGFR3-signalling specifically inhibits lymphangiogenesis in inflammatory corneal neovascularisation. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 246: 115–119 - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P 2005. Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature 438: 932–936 - PubMed
-
- Cesetti T, Obernier K, Bengtson CP, Fila T, Mandl C, Holzl-Wenig G, Worner K, Eckstein V, Ciccolini F 2009. Analysis of stem cell lineage progression in the neonatal subventricular zone identifies EGFR+/NG2− cells as transit-amplifying precursors. Stem Cells 27: 1443–1454 - PubMed
-
- Chojnacki AK, Mak GK, Weiss S 2009. Identity crisis for adult periventricular neural stem cells: subventricular zone astrocytes, ependymal cells or both? Nat Rev Neurosci 10: 153–163 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
