Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of therapeutic doses of basal insulins NPH, glargine, and detemir after 1 week of daily administration at bedtime in type 2 diabetic subjects: a randomized cross-over study
- PMID: 21498786
- PMCID: PMC3114339
- DOI: 10.2337/dc10-1911
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of therapeutic doses of basal insulins NPH, glargine, and detemir after 1 week of daily administration at bedtime in type 2 diabetic subjects: a randomized cross-over study
Abstract
Objective: To compare the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of NPH, glargine, and detemir insulins in type 2 diabetic subjects.
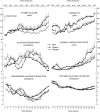
Research design and methods: This study used a single-blind, three-way, cross-over design. A total of 18 type 2 diabetic subjects underwent a euglycemic clamp for 32 h after a subcutaneous injection of 0.4 units/kg at 2200 h of either NPH, glargine, or detemir after 1 week of bedtime treatment with each insulin.
Results: The glucose infusion rate area under the curve(0-32 h) was greater for glargine than for detemir and NPH (1,538 ± 688; 1,081 ± 785; and 1,170 ± 703 mg/kg, respectively; P < 0.05). Glargine suppressed endogenous glucose production more than detemir (P < 0.05) and similarly to NPH (P = 0.16). Glucagon, C-peptide, free fatty acids, and β-hydroxy-butyrate were more suppressed with glargine than detemir. All 18 subjects completed the glargine study, but two subjects on NPH and three on detemir interrupted the study because of plasma glucose >150 mg/dL.
Conclusions: Compared with NPH and detemir, glargine provided greater metabolic activity and superior glucose control for up to 32 h.
Figures
References
-
- Hompesch M, Troupin B, Heise T, et al. Time-action profile of insulin detemir and NPH insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes from different ethnic groups. Diabetes Obes Metab 2006;8:568–573 - PubMed
-
- Linn T, Fischer B, Soydan N, et al. Nocturnal glucose metabolism after bedtime injection of insulin glargine or neutral protamine hagedorn insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008;93:3839–3846 - PubMed
-
- Porcellati F, Rossetti P, Busciantella NR, et al. Comparison of pharmacokinetics and dynamics of the long-acting insulin analogs glargine and detemir at steady state in type 1 diabetes: a double-blind, randomized, crossover study. Diabetes Care 2007;30:2447–2452 - PubMed
-
- Gastaldelli A, Coggan AR, Wolfe RR. Assessment of methods for improving tracer estimation of non-steady-state rate of appearance. J Appl Physiol 1999;87:1813–1822 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical