Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) 5-HT(2A) receptor: association with inherent and cocaine-evoked behavioral disinhibition in rats
- PMID: 21499079
- PMCID: PMC3124821
- DOI: 10.1097/FBP.0b013e328345f90d
Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) 5-HT(2A) receptor: association with inherent and cocaine-evoked behavioral disinhibition in rats
Abstract
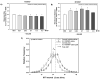
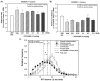
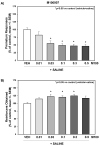
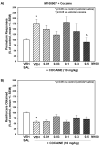
Alterations in the balance of functional activity within the serotonin [5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)] system are hypothesized to underlie impulse control. Cocaine-dependent subjects consistently show greater impulsivity relative to nondrug using control subjects. Preclinical studies suggest that the 5-HT(2A) receptor (5-HT(2A)R) contributes to the regulation of impulsive behavior and also mediates some of the behavioral effects of cocaine. We hypothesized that the selective 5-HT(2A)R antagonist M100907 would reduce inherent levels of impulsivity and attenuate impulsive responding induced by cocaine in two animal models of impulsivity, the differential reinforcement of low rate (DRL) task and the one-choice serial reaction time (1-CSRT) task. M100907 reduced rates of responding in the DRL task and premature responding in the 1-CSRT task. Conversely, cocaine disrupted rates of responding in the DRL task and increased premature responding in the 1-CSRT task. M100907 attenuated cocaine-induced increases in specific markers of behavioral disinhibition in the DRL and 1-CSRT tasks. These results suggest that the 5-HT(2A)R regulates inherent impulsivity, and that blockade of the 5-HT(2A)R alleviates specific aspects of elevated levels of impulsivity induced by cocaine exposure. These data point to the 5-HT(2A)R as an important regulatory substrate in impulse control.
Figures
References
-
- Ardayfio PA, Benvenga MJ, Chaney SF, Love PL, Catlow J, Swanson SP, Marek GJ. The 5-hydroxytryptamine2A receptor antagonist R-(+)-alpha-(2,3-dimethoxyphenyl)-1-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)ethyl-4-piperidinem ethanol (M100907) attenuates impulsivity after both drug-induced disruption (dizocilpine) and enhancement (antidepressant drugs) of differential-reinforcement-of-low-rate 72-s behavior in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;327:891–897. - PubMed
-
- Auclair A, Drouin C, Cotecchia S, Glowinski J, Tassin JP. 5-HT2A and alpha1b-adrenergic receptors entirely mediate dopamine release, locomotor response and behavioural sensitization to opiates and psychostimulants. Eur J Neurosci. 2004;20:3073–3084. - PubMed
-
- Beck LH, Bransome ED, Jr, Mirsky AF, Rosvold HE, Sarason I. A continuous performance test of brain damage. J Consult Psychol. 1956;20:343–350. - PubMed
-
- Bradberry CW, Roth RH. Cocaine increases extracellular dopamine in rat nucleus accumbens and ventral tegmental area as shown by in vivo microdiaysis. Neurosci Lett. 1989;103:97–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

