Induction of intracellular Ca2+ and pH changes in Sf9 insect cells by rhodojaponin-III, a natural botanic insecticide isolated from Rhododendron molle
- PMID: 21499219
- PMCID: PMC6260631
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules16043179
Induction of intracellular Ca2+ and pH changes in Sf9 insect cells by rhodojaponin-III, a natural botanic insecticide isolated from Rhododendron molle
Abstract
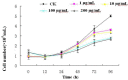
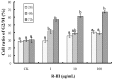
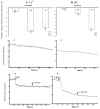
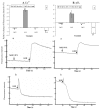
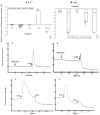
Many studies on intracellular calcium ([Ca2+](i)) and intracellular pH (pH(i)) have been carried out due to their importance in regulation of different cellular functions. However, most of the previous studies are focused on human or mammalian cells. The purpose of the present study was to characterize the effect of Rhodojaponin-III (R-III) on [Ca2+](i) and pH(i) and the proliferation of Sf9 cells. R-III strongly inhibited Sf9 cells proliferation with a time- and dose-dependent manner. Flow cytometry established that R-III interfered with Sf9 cells division and arrested them in G2/M. By using confocal scanning technique, effects of R-III on intracellular free calcium ([Ca2+](i)) and intracellular pH (pH(i)) in Sf9 cells were determined. R-III induced a significant dose-dependent (1, 10, 100, 200 μg/mL) increase in [Ca2+](i) and pH(i) of Sf9 cells in presence of Ca2+-containing solution (Hanks) and an irreversible decrease in the absence of extra cellular Ca2+. We also found that both extra cellular Ca2+ and intracellular Ca2+ stores contributed to the increase of [Ca2+](i), because completely treating Sf9 cells with CdCl(2) (5 mM), a Ca2+ channels blocker, R-III (100 μg/mL) induced a transient elevation of [Ca2+](i) in case of cells either in presence of Ca2+ containing or Ca2+ free solution. In these conditions, pH(i) showed similar changes with that of [Ca2+](i) on the whole. Accordingly, we supposed that there was a certain linkage for change of [Ca2+](i), cell cycle arrest, proliferation inhibition in Sf9 cells induced by R-III.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular cloning and functional identification of an insect odorant receptor gene in Spodoptera litura (F.) for the botanical insecticide rhodojaponin III.J Insect Physiol. 2013 Jan;59(1):26-32. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2012.11.004. Epub 2012 Nov 27. J Insect Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23195879
-
A novel method using Autographa californica multiple nucleopolyhedrovirus for increasing the sensitivity of insecticide through calcium influx in insect cell line.J Virol Methods. 2014 Jan;195:72-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2013.09.010. Epub 2013 Oct 18. J Virol Methods. 2014. PMID: 24140515
-
A COMPREHENSIVE STUDY ON APOPTOSIS INDUCTION BY AZADIRACHTIN IN Spodoptera frugiperda CULTURED CELL LINE Sf9.Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2015 Jul;89(3):153-68. doi: 10.1002/arch.21233. Epub 2015 Apr 1. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25828604
-
Autographa californica nucleopolyhedrovirus infection results in Sf9 cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase.Virology. 1998 Apr 25;244(1):195-211. doi: 10.1006/viro.1998.9097. Virology. 1998. PMID: 9581791
-
Changes in intracellular Ca2+ concentration produced by the alteration of intracellular pH in rat parotid acinar cells.Jpn J Physiol. 1997 Feb;47(1):41-9. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.47.41. Jpn J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9159641 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of Rhododendri Mollis Flos and its representative component as a potential analgesic.J Nat Med. 2024 Jun;78(3):753-767. doi: 10.1007/s11418-024-01815-0. Epub 2024 Apr 26. J Nat Med. 2024. PMID: 38668831
-
Rhododendron molle G. Don Extract Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Migration in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells and Potential Anticancer Components Analysis.Molecules. 2021 May 18;26(10):2990. doi: 10.3390/molecules26102990. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34069900 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the interplay between root exudates, microbiota, and rhizosheath formation in pearl millet.Microbiome. 2024 Jan 3;12(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s40168-023-01727-3. Microbiome. 2024. PMID: 38167150 Free PMC article.
-
Insect Cell-Based Models: Cell Line Establishment and Application in Insecticide Screening and Toxicology Research.Insects. 2023 Jan 18;14(2):104. doi: 10.3390/insects14020104. Insects. 2023. PMID: 36835673 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Klocke J.A., Hu M.Y., Chiu S.F., Kubo I. Grayanoid diterpenes insect antifeedants and insecticides from Rhododendron molle. Phytochemistry. 1991;30:1797–1800. doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(91)85015-R. - DOI
-
- Hu M.Y., Zhong G.H., Wu Q.S., Chiu S.F. The biological activities of yellow azalea, Rhododendron molle G. Don against the vegetable leafminer, Liriomyza sativae (Diptera: Agromyzidae) Entomologia Sinica. 2000;7:65–70.
-
- Zhong G.H., Hu M.Y., Chiu S.F., Cheng D.M. Effects of Rhodojaponin-III on nervous System of larvae of imported cabbage worm, Pieris rapae L. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2000;2:13–18.
-
- Feng X., Chiu S.F. Preliminary studies on the biological activity of extracts from Rhododendron molle against insect pests and their mode of action. J. South China Agric. Univ. 1990;11:135–142.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

