NFIL3/E4BP4 controls type 2 T helper cell cytokine expression
- PMID: 21499227
- PMCID: PMC3098483
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2011.111
NFIL3/E4BP4 controls type 2 T helper cell cytokine expression
Abstract
Type 2 T helper (T(H)2) cells are critical for the development of allergic immune responses; however, the molecular mechanism controlling their effector function is still largely unclear. Here, we report that the transcription factor NFIL3/E4BP4 regulates cytokine production and effector function by T(H)2 cells. NFIL3 is highly expressed in T(H)2 cells but much less in T(H)1 cells. Production of interleukin (IL)-13 and IL-5 is significantly increased in Nfil3(-/-) T(H)2 cells and is decreased by expression of NFIL3 in wild-type T(H)2 cells. NFIL3 directly binds to and negatively regulates the Il13 gene. In contrast, IL-4 production is decreased in Nfil3(-/-) T(H)2 cells. Increased IL-13 and IL-5 together with decreased IL-4 production by antigen-stimulated splenocytes from the immunized Nfil3(-/-) mice was also observed. The ability of NFIL3 to alter T(H)2 cytokine production is a T-cell intrinsic effect. Taken together, these data indicate that NFIL3 is a key regulator of T(H)2 responses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
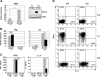
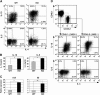

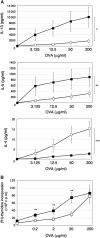
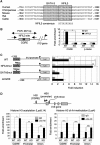

References
-
- Agarwal S, Rao A (1998) Modulation of chromatin structure regulates cytokine gene expression during T cell differentiation. Immunity 9: 765–775 - PubMed
-
- Altura RA, Inukai T, Ashmun RA, Zambetti GP, Roussel MF, Look AT (1998) The chimeric E2A-HLF transcription factor abrogates p53-induced apoptosis in myeloid leukemia cells. Blood 92: 1397–1405 - PubMed
-
- Ansel KM, Djuretic I, Tanasa B, Rao A (2006) Regulation of Th2 differentiation and Il4 locus accessibility. Annu Rev Immunol 24: 607–656 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

