Suppression of TH17 differentiation and autoimmunity by a synthetic ROR ligand
- PMID: 21499262
- PMCID: PMC3148894
- DOI: 10.1038/nature10075
Suppression of TH17 differentiation and autoimmunity by a synthetic ROR ligand
Abstract
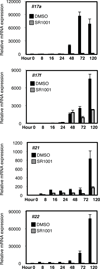
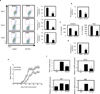
T-helper cells that produce interleukin-17 (T(H)17 cells) are a recently identified CD4(+) T-cell subset with characterized pathological roles in autoimmune diseases. The nuclear receptors retinoic-acid-receptor-related orphan receptors α and γt (RORα and RORγt, respectively) have indispensible roles in the development of this cell type. Here we present SR1001, a high-affinity synthetic ligand-the first in a new class of compound-that is specific to both RORα and RORγt and which inhibits T(H)17 cell differentiation and function. SR1001 binds specifically to the ligand-binding domains of RORα and RORγt, inducing a conformational change within the ligand-binding domain that encompasses the repositioning of helix 12 and leads to diminished affinity for co-activators and increased affinity for co-repressors, resulting in suppression of the receptors' transcriptional activity. SR1001 inhibited the development of murine T(H)17 cells, as demonstrated by inhibition of interleukin-17A gene expression and protein production. Furthermore, SR1001 inhibited the expression of cytokines when added to differentiated murine or human T(H)17 cells. Finally, SR1001 effectively suppressed the clinical severity of autoimmune disease in mice. Our data demonstrate the feasibility of targeting the orphan receptors RORα and RORγt to inhibit specifically T(H)17 cell differentiation and function, and indicate that this novel class of compound has potential utility in the treatment of autoimmune diseases.
Figures


Comment in
-
Immunology: A helping hand against autoimmunity.Nature. 2011 Apr 28;472(7344):421-2. doi: 10.1038/472421a. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21525918 Free PMC article.
-
Autoimmune disease: Blocking the drivers.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011 Jun;10(6):413. doi: 10.1038/nrd3467. Epub 2011 May 20. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011. PMID: 21597470 No abstract available.
References
-
- McGeachy MJ, Cua DJ. Th17 cell differentiation: The long and winding road. Immunity. 2008;28:445–453. - PubMed
-
- Littman DR, Rudensky AY. Th17 and Regulatory T Cells in Mediating and Restraining Inflammation. Cell. 140:845–858. - PubMed
-
- Ivanov II, et al. The orphan nuclear receptor ROR gamma t directs the differentiation program of proinflammatory IL-17(+) T helper cells. Cell. 2006;126:1121–1133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

