B cells promote insulin resistance through modulation of T cells and production of pathogenic IgG antibodies
- PMID: 21499269
- PMCID: PMC3270885
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2353
B cells promote insulin resistance through modulation of T cells and production of pathogenic IgG antibodies
Abstract
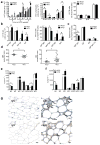
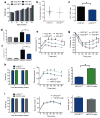
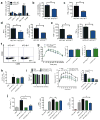
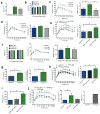
Chronic inflammation characterized by T cell and macrophage infiltration of visceral adipose tissue (VAT) is a hallmark of obesity-associated insulin resistance and glucose intolerance. Here we show a fundamental pathogenic role for B cells in the development of these metabolic abnormalities. B cells accumulate in VAT in diet-induced obese (DIO) mice, and DIO mice lacking B cells are protected from disease despite weight gain. B cell effects on glucose metabolism are mechanistically linked to the activation of proinflammatory macrophages and T cells and to the production of pathogenic IgG antibodies. Treatment with a B cell-depleting CD20 antibody attenuates disease, whereas transfer of IgG from DIO mice rapidly induces insulin resistance and glucose intolerance. Moreover, insulin resistance in obese humans is associated with a unique profile of IgG autoantibodies. These results establish the importance of B cells and adaptive immunity in insulin resistance and suggest new diagnostic and therapeutic modalities for managing the disease.
Figures
Comment in
-
The B-side story in insulin resistance.Nat Med. 2011 May;17(5):539-40. doi: 10.1038/nm0511-539. Nat Med. 2011. PMID: 21546966 No abstract available.
-
The bigger B cell picture.Nat Rev Immunol. 2016 Mar;16(3):133. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.3. Epub 2016 Jan 25. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26806483 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

