Multiple biomarker expression on circulating tumor cells in comparison to tumor tissues from primary and metastatic sites in patients with locally advanced/inflammatory, and stage IV breast cancer, using a novel detection technology
- PMID: 21499685
- PMCID: PMC3543871
- DOI: 10.1007/s10549-011-1508-0
Multiple biomarker expression on circulating tumor cells in comparison to tumor tissues from primary and metastatic sites in patients with locally advanced/inflammatory, and stage IV breast cancer, using a novel detection technology
Abstract
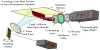
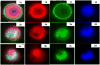
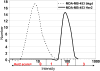
Patients with locally advanced/inflammatory breast cancer (LABC/IBC) face a high likelyhood of recurrence and prognosis for relapsed, or de novo stage IV metastatic breast cancer (MBC) remains poor. Estrogen (ER) and HER2 receptor expression on primary or MBC allow targeted therapies, but an estimated 10-18% of tumors do not exhibit these biomarkers and survival in these cases is even poorer. Variations in discordance rates for the expression of ER and HER2 receptors have been observed between primary and metastatic tumors and such discordances may lead to suboptimal treatment. Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) are considered the seeds of residual disease and distant metastases and their characterization could help guide treatment selection. To explore this possibility, we used multiple biomarker assessment of CTCs in comparison to primary and metastatic tumor sites. Thirty-six patients with LABC/IBC, or stage IV MBC were evaluated. Blood samples were procured prior to initiating or changing therapy. CTCs were identified based on presence of cytokeratin and nucleus staining, and the absence of CD45. A multimarker assay was developed to simultaneously quantify expression of HER2, ER, and ERCC1, a DNA excision repair protein. Novel fiber-optic array scanning technology (FAST) was used for sensitive location of CTCs. CTCs were detected in 82% of MBC and 62% LABC/IBC cases. Multiplex marker expression was successfully carried out in samples from18 patients with MBC and in 8 patients with LABC/IBC that contained CTCs. In MBC, we detected actionable discordance rates of 40 and 23%, respectively for ER and HER2 where a biomarker was negative in the primary or metastatic tumor and positive in the CTCs. In LABC/IBC, actionable discordances were 60 and 20% for ER and HER2, respectively. Pilot trials evaluating the effectiveness of treatment selections based on actionable discordances between biomarker expression patterns on CTCs and primary or metastatic tumor sites may allow for a prospective assessment of CTC-based individualized targeted therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare for any of the authors involved in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA, Fluge O, Pergamenschikov A, Williams C, Zhu SX, Lonning PE, Borresen-Dale AL, Brown PO, Botstein D. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406(6797):747–752. doi: 10.1038/35021093. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chia SK, Speers CH, D'Yachkova Y, Kang A, Malfair-Taylor S, Barnett J, Coldman A, Gelmon KA, O'Reilly SE, Olivotto IA. The impact of new chemotherapeutic and hormone agents on survival in a population-based cohort of women with metastatic breast cancer. Cancer. 2007;110(5):973–979. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22867. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Robert N, Leyland-Jones B, Asmar L, Belt R, Ilegbodu D, Loesch D, Raju R, Valentine E, Sayre R, Cobleigh M, Albain K, McCullough C, Fuchs L, Slamon D. Randomized phase III study of trastuzumab, paclitaxel, and carboplatin compared with trastuzumab and paclitaxel in women with HER-2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(18):2786–2792. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2005.04.1764. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

